Diagnostic Dilemma of Biliopancreatic Contrast-Enhanced Harmonic Endoscopic Ultrasonography
- PMID: 36010332
- PMCID: PMC9406750
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12081983
Diagnostic Dilemma of Biliopancreatic Contrast-Enhanced Harmonic Endoscopic Ultrasonography
Abstract
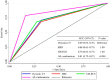
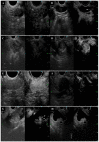
Background: The utility of contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasonography (CH-EUS) alone in the biliopancreatic region appears to be limited because it is highly dependent on the experience and skill of the endoscopist. Therefore, the present study aimed to validate the efficacy of CH-EUS in clinical practice. Methods: Between January 2018 and March 2019, 301 consecutive patients who underwent CH-EUS were prospectively enrolled in this study. The diagnostic performance of CH-EUS was compared with that of dynamic computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and all combinations (i.e., CH-EUS, dynamic CT, and MRI) using a Bonferroni correction. A multiple logistic regression analysis was performed to extract each disease that allowed the CH-EUS diagnosis to be consistent with the final diagnosis. Results: In multiple comparisons of diagnostic performance, no significant differences were observed among dynamic CT, MRI, and CH-EUS (p = 1.00), but the diagnostic performance was significantly higher when all modalities were combined (p < 0.001). Moreover, only intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm comprising adenoma or carcinoma (IPMN, n = 161) showed significance with respect to the agreement with the final diagnosis (p = 0.006). Conclusions: Our results showed that CH-EUS-based diagnosis of IPMN may be possible in clinical practice. On the contrary, to accurately diagnose biliopancreatic diseases other than IPMN, comprehensive diagnosis using multiple modalities may be necessary, rather than relying on CH-EUS alone.
Keywords: biliary tract diseases; diagnostic performance; endosonography; pancreatic diseases; ultrasound contrast agents.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Value of additional endoscopic ultrasonography for surveillance after surgical removal of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms.Dig Endosc. 2018 Sep;30(5):659-666. doi: 10.1111/den.13176. Epub 2018 May 16. Dig Endosc. 2018. PMID: 29675938
-
Usefulness of Contrast-Enhanced Harmonic Endoscopic Ultrasonography for Diagnosis of Malignancy in Intraductal Papillary Mucinous Neoplasm.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Sep 2;12(9):2141. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12092141. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36140542 Free PMC article.
-
Contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasonography for pancreatobiliary diseases.Dig Endosc. 2015 Apr;27 Suppl 1:60-7. doi: 10.1111/den.12454. Dig Endosc. 2015. PMID: 25639788 Review.
-
Can contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasonography accurately diagnose main pancreatic duct involvement in intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms?Pancreatology. 2020 Jul;20(5):887-894. doi: 10.1016/j.pan.2020.06.004. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Pancreatology. 2020. PMID: 32651080
-
Use of contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasonography for the diagnosis of pancreatic cystic lesions.J Med Ultrason (2001). 2023 Nov 4. doi: 10.1007/s10396-023-01376-x. Online ahead of print. J Med Ultrason (2001). 2023. PMID: 37924442 Review.
References
-
- Lisotti A., Napoleon B., Facciorusso A., Cominardi A., Crino S.F., Brighi N., Gincul R., Kitano M., Yamashita Y., Marchegiani G., et al. Contrast-enhanced EUS for the characterization of mural nodules within pancreatic cystic neoplasms: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021;94:881–889. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2021.06.028. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ishikawa R., Kamata K., Hara A., Tanaka H., Okamoto A., Yamazaki T., Nakai A., Omoto S., Minaga K., Yamao K., et al. Utility of contrast-enhanced harmonic endoscopic ultrasonography for predicting the prognosis of pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms. Dig. Endosc. 2021;33:829–839. doi: 10.1111/den.13862. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fusaroli P., Napoleon B., Gincul R., Lefort C., Palazzo L., Palazzo M., Kitano M., Minaga K., Caletti G., Lisotti A. The clinical impact of ultrasound contrast agents in EUS: A systematic review according to the levels of evidence. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2016;84:587–596. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2016.06.006. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

