Reproducibility and Repeatability of Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CCTA) Image Segmentation in Detecting Atherosclerosis: A Radiomics Study
- PMID: 36010355
- PMCID: PMC9406887
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12082007
Reproducibility and Repeatability of Coronary Computed Tomography Angiography (CCTA) Image Segmentation in Detecting Atherosclerosis: A Radiomics Study
Abstract
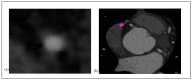
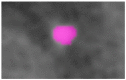
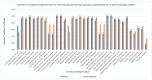
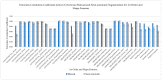
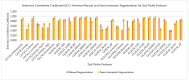
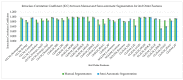
Atherosclerosis is known as the leading factor in heart disease with the highest mortality rate among the Malaysian population. Usually, the gold standard for diagnosing atherosclerosis is by using the coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) technique to look for plaque within the coronary artery. However, qualitative diagnosis for noncalcified atherosclerosis is vulnerable to false-positive diagnoses, as well as inconsistent reporting between observers. In this study, we assess the reproducibility and repeatability of segmenting atherosclerotic lesions manually and semiautomatically in CCTA images to identify the most appropriate CCTA image segmentation method for radiomics analysis to quantitatively extract the atherosclerotic lesion. Thirty (30) CCTA images were taken retrospectively from the radiology image database of Hospital Canselor Tuanku Muhriz (HCTM), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. We extract 11,700 radiomics features which include the first-order, second-order and shape features from 180 times of image segmentation. The interest vessels were segmentized manually and semiautomatically using LIFEx (Version 7.0.15, Institut Curie, Orsay, France) software by two independent radiology experts, focusing on three main coronary blood vessels. As a result, manual segmentation with a soft-tissuewindowing setting yielded higher repeatability as compared to semiautomatic segmentation with a significant intraclass correlation coefficient (intra-CC) 0.961 for thefirst-order and shape features; intra-CC of 0.924 for thesecond-order features with p < 0.001. Meanwhile, the semiautomatic segmentation has higher reproducibility as compared to manual segmentation with significant interclass correlation coefficient (inter-CC) of 0.920 (first-order features) and a good interclass correlation coefficient of 0.839 for the second-order features with p < 0.001. The first-order, shape order and second-order features for both manual and semiautomatic segmentation have an excellent percentage of reproducibility and repeatability (intra-CC > 0.9). In conclusion, semi-automated segmentation is recommended for inter-observer study while manual segmentation with soft tissue-windowing can be used for single observer study.
Keywords: CCTA; atherosclerosis; radiomics; repeatability; reproducibility.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Auto-segmentation, radiomic reproducibility, and comparison of radiomics between manual and AI-derived segmentations for coronary arteries in cardiac [18F]NaF PET/CT images.EJNMMI Phys. 2025 Apr 27;12(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s40658-025-00751-6. EJNMMI Phys. 2025. PMID: 40287890 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of pathology-confirmed vulnerable atherosclerotic lesions by coronary computed tomography angiography using radiomics analysis.Eur Radiol. 2022 Jun;32(6):4003-4013. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-08518-0. Epub 2022 Feb 16. Eur Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35171348
-
Reliability of MRI radiomics features in MR-guided radiotherapy for prostate cancer: Repeatability, reproducibility, and within-subject agreement.Med Phys. 2021 Nov;48(11):6976-6986. doi: 10.1002/mp.15232. Epub 2021 Sep 25. Med Phys. 2021. PMID: 34562286
-
Cardiac computed tomography radiomics: an emerging tool for the non-invasive assessment of coronary atherosclerosis.Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2020 Dec;10(6):2005-2017. doi: 10.21037/cdt-20-156. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 2020. PMID: 33381440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From CT to artificial intelligence for complex assessment of plaque-associated risk.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020 Dec;36(12):2403-2427. doi: 10.1007/s10554-020-01926-1. Epub 2020 Jul 2. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32617720 Review.
Cited by
-
Auto-segmentation, radiomic reproducibility, and comparison of radiomics between manual and AI-derived segmentations for coronary arteries in cardiac [18F]NaF PET/CT images.EJNMMI Phys. 2025 Apr 27;12(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s40658-025-00751-6. EJNMMI Phys. 2025. PMID: 40287890 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Radiomics Features Based on H&E Images as Potential Biomarkers for Evaluating Muscle Atrophy: A Preliminary Study.J Imaging Inform Med. 2024 Oct;37(5):2324-2341. doi: 10.1007/s10278-024-01122-w. Epub 2024 Apr 23. J Imaging Inform Med. 2024. PMID: 38653909 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Image Enhancement on the Radiomics Stability of Diffusion-Weighted MRI Images of Cervical Cancer.Cureus. 2024 Jan 11;16(1):e52132. doi: 10.7759/cureus.52132. eCollection 2024 Jan. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38347995 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review and meta-analysis on the classification metrics of machine learning algorithm based radiomics in hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 14;10(16):e36313. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36313. eCollection 2024 Aug 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39253167 Free PMC article.
-
Stability and Reproducibility of Radiomic Features Based on Various Segmentation Techniques on Cervical Cancer DWI-MRI.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Dec 12;12(12):3125. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12123125. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36553132 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO The Top 10 Causes of Death. [(accessed on 2 June 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/the-top-10-causes-of-death.
-
- Cury R.C., Abbara S., Achenbach S., Agatston A., Berman D.S., Budoff M.J., Dill K.E., Jacobs J.E., Maroules C.D., Rubin G.D., et al. CAD-RADSTM Coronary Artery Disease—Reporting and Data System. An Expert Consensus Document of the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography (SCCT), the American College of Radiology (ACR) and the North American Society for Cardiovascular Imaging (NASCI). Endorsed by the American College of Cardiology. J. Cardiovasc. Comput. Tomogr. 2016;10:269–281. doi: 10.1016/j.jcct.2016.04.005. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Newby D., Williams M., Hunter A., Pawade T., Shah A., Flapan A., Forbes J., Hargreaves A., Leslie S., Lewis S., et al. CT Coronary Angiography in Patients with Suspected Angina Due to Coronary Heart Disease (SCOT-HEART): An Open-Label, Parallel-Group, Multicentre Trial. Lancet. 2015;385:2383–2391. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60291-4. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

