Assessment of Pulpal Status in Primary Teeth Following Direct Pulp Capping in an Experimental Canine Model
- PMID: 36010372
- PMCID: PMC9407383
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics12082022
Assessment of Pulpal Status in Primary Teeth Following Direct Pulp Capping in an Experimental Canine Model
Abstract
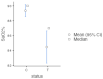
(1) Background: This study aimed to assess the pulpal response of primary teeth by pulse-oximetry (PO) in a canine model, following direct pulp capping (DPC). (2) Methods: Forty-eight primary teeth from eight canine subjects were divided into three treatment groups, based on the DPC material—calcium hydroxide (CH), MTA, BiodentineTM)—and three corresponding control groups. Data from PO pulp testing were correlated with laser Doppler flowmetry (LDF) testing, computer tomographic (CT) densitometry and histological analysis; the experiment lasted 14 days. (3) Results: SpO₂ recordings revealed statistically significant differences (p = 0.002, <0.05) between the treatment and control groups, and no significant differences (p = 0.257, >0.05) were observed between treatment groups. LDF recordings showed significant differences (p = 0.002, <0.05) between the treatment and control groups and identified significant differences between materials (p = 0.001, <0.05). CT densitometry indicated vital pulps in all teeth, with pulpal inflammation detected in 6/8 CH-capped teeth and 2/8 MTA-capped teeth. Histologic evaluation confirmed vital pulp in all specimens, with different degrees of inflammation. (4) Conclusions: Within its limitations, the present study confirms the diagnostic value of PO evaluation of pulpal status in primary teeth with histologic means after pulp-capping procedures in a canine model. However, various degrees of pulpal inflammation elicited by different pulp-capping materials seem not to correlate with the obtained PO values.
Keywords: LDF; pulp capping; pulse oximetry; vitality pulp testing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry . The Reference Manual of Pediatric Dentistry. 3rd ed. American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry; Chicago, IL, USA: 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

