Advances in the Formation and Control Methods of Undesirable Flavors in Fish
- PMID: 36010504
- PMCID: PMC9407384
- DOI: 10.3390/foods11162504
Advances in the Formation and Control Methods of Undesirable Flavors in Fish
Abstract
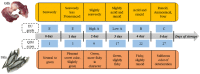
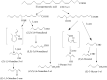
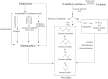
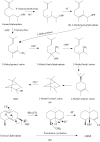
Undesirable flavor formation in fish is a dynamic biological process, decreasing the overall flavor quality of fish products and impeding the sale of fresh fish. This review extensively summarizes chemical compounds contributing to undesirable flavors and their sources or formation. Specifically, hexanal, heptanal, nonanal, 1-octen-3-ol, 1-penten-3-ol, (E,E)-2,4-heptadienal, (E,E)-2,4-decadienal, trimethylamine, dimethyl sulfide, 2-methyl-butanol, etc., are characteristic compounds causing off-odors. These volatile compounds are mainly generated via enzymatic reactions, lipid autoxidation, environmentally derived reactions, and microbial actions. A brief description of progress in existing deodorization methods for controlling undesirable flavors in fish, e.g., proper fermenting, defatting, appropriate use of food additives, and packaging, is also presented. Lastly, we propose a developmental method regarding the multifunctional natural active substances made available during fish processing or packaging, which hold great potential in controlling undesirable flavors in fish due to their safety and efficiency in deodorization.
Keywords: deodorization; lipid oxidation; microorganism; natural active substances; undesirable flavor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Research progress of fishy odor in aquatic products: From substance identification, formation mechanism, to elimination pathway.Food Res Int. 2024 Feb;178:113914. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2023.113914. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Food Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38309863 Review.
-
Iron-lactoferrin complex reduces iron-catalyzed off-flavor formation in powdered milk with added fish oil.J Food Sci. 2012 Aug;77(8):C853-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2012.02809.x. J Food Sci. 2012. PMID: 22860577
-
The role of ultraviolet radiation in the flavor formation during drying processing of Pacific saury (Cololabis saira).J Sci Food Agric. 2024 Oct;104(13):8099-8108. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.13640. Epub 2024 Jun 10. J Sci Food Agric. 2024. PMID: 38856111
-
Improving the flavor of tilapia fish head soup by adding lipid oxidation products and cysteine.Food Chem. 2023 Dec 15;429:136976. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.136976. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Food Chem. 2023. PMID: 37517226
-
Flavor Formation in Dry-Cured Fish: Regulation by Microbial Communities and Endogenous Enzymes.Foods. 2023 Aug 11;12(16):3020. doi: 10.3390/foods12163020. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37628021 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Volatilome Analysis and Evolution in the Headspace of Packed Refrigerated Fish.Foods. 2023 Jul 10;12(14):2657. doi: 10.3390/foods12142657. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37509749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) for Seaweed Conservation: Impact on Physicochemical Characteristics and Microbiological Activity.Foods. 2023 Jul 18;12(14):2736. doi: 10.3390/foods12142736. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37509828 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Antimicrobial and Preservative Effects of Cinnamaldehyde and Clove Oil in Catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) Fillets Stored at 4 °C.Foods. 2024 May 8;13(10):1445. doi: 10.3390/foods13101445. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38790745 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Different Water Contents on the Quality Characteristics of Roasted Large Yellow Croaker (Larimichthys crocea) Fillets.Foods. 2025 May 7;14(9):1638. doi: 10.3390/foods14091638. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40361721 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative flavoromics-GC-MS/IMS approach to study the formation mechanism of fishy flavor in skipjack tuna oil induced by oxidation and heat.Food Chem X. 2025 May 22;28:102577. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2025.102577. eCollection 2025 May. Food Chem X. 2025. PMID: 40502417 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Smith J.L., Boyer G.L., Zimba P.V. A review of cyanobacterial odorous and bioactive metabolites: Impacts and management alternatives in aquaculture. Aquaculture. 2008;280:5–20. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2008.05.007. - DOI
-
- An Y., Qian Y.L., Alcazar Magana A., Xiong S., Qian M.C. Comparative characterization of aroma compounds in silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix), pacific whiting (Merluccius productus), and alaska pollock (Theragra chalcogramma) surimi by aroma extract dilution analysis, odor activity value, and aroma recombination studies. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2020;68:10403–10413. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

