Untargeted Multimodal Metabolomics Investigation of the Haemonchus contortus Exsheathment Secretome
- PMID: 36010603
- PMCID: PMC9406637
- DOI: 10.3390/cells11162525
Untargeted Multimodal Metabolomics Investigation of the Haemonchus contortus Exsheathment Secretome
Abstract
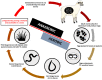
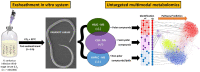
In nematodes that invade the gastro-intestinal tract of the ruminant, the process of larval exsheathment marks the transition from the free-living to the parasitic stages of these parasites. To investigate the secretome associated with larval exsheathment, a closed in vitro system that effectively reproduces the two basic components of an anaerobic rumen environment (CO2 and 39 °C) was developed to trigger exsheathment in one of the most pathogenic and model gastrointestinal parasitic nematodes, Haemonchus contortus (barber's pole worm). This study reports the use of multimodal untargeted metabolomics and lipidomics methodologies to identify the metabolic signatures and compounds secreted during in vitro larval exsheathment in the H. contortus infective third-stage larva (iL3). A combination of statistical and chemoinformatic analyses using three analytical platforms revealed a panel of metabolites detected post exsheathment and associated with amino acids, purines, as well as select organic compounds. The major lipid classes identified by the non-targeted lipidomics method applied were lysophosphatidylglycerols, diglycerides, fatty acyls, glycerophospholipids, and a triglyceride. The identified metabolites may serve as metabolic signatures to improve tractability of parasitic nematodes for characterizing small molecule host-parasite interactions related to pathogenesis, vaccine and drug design, as well as the discovery of metabolic biomarkers.
Keywords: Haemonchus contortus; exsheathment; helminth; lipidomics; metabolomics; parasite.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Besier R., Kahn L., Sargison N., Van Wyk J. Diagnosis, treatment and management of Haemonchus contortus in small ruminants. Adv. Parasitol. 2016;93:181–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

