Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Lung Cancer with a Risk-Adapted Strategy Using the Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy Technique: A Single Arm Phase II Study
- PMID: 36010985
- PMCID: PMC9406332
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14163993
Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Lung Cancer with a Risk-Adapted Strategy Using the Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy Technique: A Single Arm Phase II Study
Abstract
Purpose: A phase II study carried out to assess the efficacy of a risk-adapted strategy of stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) for lung cancer. The primary endpoint was 3-year local recurrence, and the secondary endpoints were overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS), rate of start of systemic therapy or best supportive care (SST-BSC), and toxicity.
Materials and methods: Eligible patients fulfilled the following criteria: performance status of 2 or less, forced expiratory volume in 1 s of 700 mL or more, and tumor not located in central or attached to the chest wall. Twenty-eight Gy was prescribed for primary lung cancers with diameters of 3 cm or less and 30 Gy was prescribed for primary lung cancers with diameters of 3.1-5.0 cm or solitary metastatic lung cancer diameters of 5 cm or less.
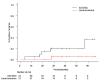
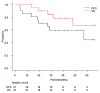
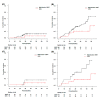
Results: Twenty-one patients were analyzed. The patients included 7 patients with adenocarcinoma, 2 patients with squamous cell carcinoma, 1 patient with metastasis, and 11 patients with clinical diagnosis. The median tumor diameter was 1.9 cm. SRS was prescribed at 28 Gy for 18 tumors and 30 Gy for 3 tumors. During the median follow-up period of 38.9 months for survivors, 1 patient had local recurrence, 7 patients had regional or distant metastasis, and 5 patients died. The 3-year local recurrence, SST-BSC, DFS, and OS rates were 5.3% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.3-22.2%), 20.1% (95% CI: 6.0-40.2%), 59.2% (95% CI: 34.4-77.3%), and 78.2% (95% CI: 51.4-91.3%), respectively. The 95% CI upper value of local recurrence was lower than the null local recurrence probability. There was no severe toxicity, and grade 2 radiation pneumonitis occurred in 1 patient.
Conclusions: Patients who received SRS for lung cancer had a low rate of 3-year local recurrence and tolerable toxicity.
Keywords: SRS; lung cancer; stereotactic body radiotherapy; stereotactic radiosurgery; volumetric modulated arc therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
T.Y., Y.K. (Yu Katagiri), Y.T. and R.S. have received lecturer fees from AstraZeneca KK. E.M. has received grants from Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. and Eli Lily Japan KK, honoraria from AstraZeneca KK, Taiho Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo KK, Boehringer Ingelheim Japan Inc., Bristol Myers Squibb Co., Ltd., Novartis Pharma KK, MSD KK, Kyowa Kirin Co Ltd., Merck Biopharma Co., Ltd., Pfizer Inc., Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Kyowa Kirin Co., Ltd., Otsuka pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. and Towa Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., and EM has been advisory board of Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., BoehringerIngelheim Japan Inc. and Eli Lilly Japan KK. K.J. has received consulting fees from Varian Medical Systems and Elekta, and honoraria from Shimazu. Co. H.M., R.U., Y.K. (Yoshiyuki Katsuta), N.K., N.T., Y.S., K.T., K.K. and S.O. have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ball D., Mai G.T., Vinod S., Babington S., Ruben J., Kron T., Chesson B., Herschtal A., Vanevski M., Rezo A., et al. TROG 09.02 CHISEL investigators. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy versus standard radiotherapy in stage 1 non-small-cell lung cancer (TROG 09.02 CHISEL): A phase 3, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019;20:494–503. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30896-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bartl A.J., Mahoney M., Hennon M.W., Yendamuri S., Videtic G.M.M., Stephans K.L., Siva S., Farrugia M.K., Ma S.J., Singh A.K. Systematic review of single-fraction stereotactic body radiation therapy for early stage non-small-cell lung cancer and lung oligometastases: How to stop worrying and love one and done. Cancers. 2022;14:790. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030790. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto T., Niibe Y., Aoki M., Shintani T., Yamada K., Kobayashi M., Yamashita H., Ozaki M., Manabe Y., Onishi H., et al. Analyses of the local control of pulmonary Oligometastases after stereotactic body radiotherapy and the impact of local control on survival. BMC Cancer. 2020;20:997. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07514-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Videtic G.M., Hu C., Singh A.K., Chang J.Y., Parker W., Olivier K.R., Schild S.E., Komaki R., Urbanic J.J., Timmerman R.D., et al. A randomized phase 2 study comparing 2 stereotactic body radiation therapy schedules for medically inoperable patients with stage I peripheral non-small cell lung cancer: NRG oncology RTOG 0915 (NCCTG N0927) Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015;93:757–764. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.07.2260. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

