Current Imaging Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 36010991
- PMCID: PMC9406360
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers14163997
Current Imaging Diagnosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fourth leading cause of cancer related death worldwide. Radiology has traditionally played a central role in HCC management, ranging from screening of high-risk patients to non-invasive diagnosis, as well as the evaluation of treatment response and post-treatment follow-up. From liver ultrasonography with or without contrast to dynamic multiple phased CT and dynamic MRI with diffusion protocols, great progress has been achieved in the last decade. Throughout the last few years, pathological, biological, genetic, and immune-chemical analyses have revealed several tumoral subtypes with diverse biological behavior, highlighting the need for the re-evaluation of established radiological methods. Considering these changes, novel methods that provide functional and quantitative parameters in addition to morphological information are increasingly incorporated into modern diagnostic protocols for HCC. In this way, differential diagnosis became even more challenging throughout the last few years. Use of liver specific contrast agents, as well as CT/MRI perfusion techniques, seem to not only allow earlier detection and more accurate characterization of HCC lesions, but also make it possible to predict response to treatment and survival. Nevertheless, several limitations and technical considerations still exist. This review will describe and discuss all these imaging modalities and their advances in the imaging of HCC lesions in cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic livers. Sensitivity and specificity rates, method limitations, and technical considerations will be discussed.
Keywords: MR diffusion imaging; computed tomography (CT); contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS); diagnostic algorithms; hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); locoregional treatment; magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); multiparametric imaging; perfusion imaging; ultrasound (US).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
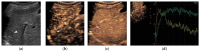
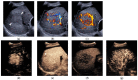

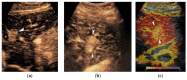


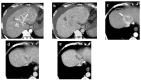
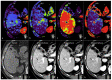
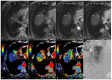
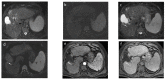
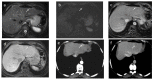


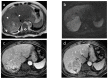
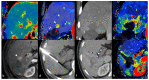
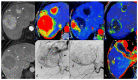
References
-
- Global Cancer Observatory. [(accessed on 5 August 2022)]. Available online: http://globocan.iarc.fr/Default.aspx.
-
- Rumgay H., Shield K., Charvat H., Ferrari P., Sornpaisarn B., Obot I., Islami F., Lemmens V.E.P.P., Rehm J., Soerjomataram I. Global burden of cancer in 2020 attributable to alcohol consumption: A population-based study. Lancet Oncol. 2021;22:1071–1080. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00279-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Marrero J.A., Kulik L.M., Sirlin C.B., Zhu A.X., Finn R.S., Abecassis M.M., Roberts L.R., Heimbach J.K. Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2018 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018;68:723–750. doi: 10.1002/hep.29913. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Omata M., Cheng A.-L., Kokudo N., Kudo M., Lee J.M., Jia J., Tateishi R., Han K.-H., Chawla Y.K., Shiina S., et al. Asia–Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: A 2017 update. Hepatol. Int. 2017;11:317–370. doi: 10.1007/s12072-017-9799-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

