Effects of Burosumab Treatment on Two Siblings with X-Linked Hypophosphatemia. Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 36011303
- PMCID: PMC9407333
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13081392
Effects of Burosumab Treatment on Two Siblings with X-Linked Hypophosphatemia. Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
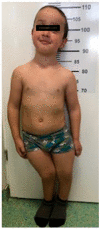
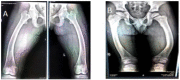
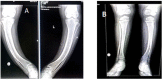
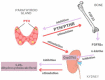
X-linked hypophosphatemia (XLH) or vitamin D-resistant rickets (MIM#307800), is a monogenic disorder with X-linked inheritance. It is caused by mutations present in the Phosphate Regulating Endopeptidase Homolog X-Linked (PHEX) gene responsible for the degradation of the bone-derived hormone fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) into inactive fragments, but the entire mechanism is currently unclear. The inactivation of the gene prevents the degradation of FGF23, causing increased levels of FGF23, which leads to decreased tubular reabsorbtion of phosphorus. Clinical aspects are growth delay, limb deformities, bone pain, osteomalacia, dental anomalies, and enthesopathy. Laboratory evaluation shows hypophosphatemia, elevated alkaline phosphatase (ALP), and normal serum calcium levels, whereas parathormone (PTH) may be normal or increased and FGF23 greatly increased. Conventional treatment consists of administration of oral phosphate and calcitriol. Treatment with Burosumab, a monoclonal antibody that binds to FGF23, reducing its activity, was approved in 2018. Methods. We describe a case of two siblings, a girl and a boy, diagnosed with XLH, monitored by the Genetic Department of the County Emergency Clinical Hospital since 2019. The clinical picture is suggestive for XLH, both siblings exhibiting short stature, lower limb curvature, bone pain, marked walking weakness, and fatigue. Radiological aspects showed marked deformity of the lower limbs: genu varum in the girl, genu varum and valgum in the boy. Laboratory investigations showed hypophosphathemia, hyperphosphaturia, elevated ALP, normal PTH, and highly increased FGF23 in both. DNA analysis performed on the two siblings revealed a nonsense mutation in exone 5 of the PHEX gene: NM_000444.6(PHEX):c.565C > T (p.Gln189Ter). Results. At the age of 13½ on 7 June 2021, the two children started treatment with Burosumab in therapeutic doses and were monitored clinically and biochemically at regular intervals according to the protocol established by the Endocrinology Commission of the Romanian Health Ministry. Conclusions. The first results of the Burosumab treatment in the two siblings are extremely encouraging and suggest a favorable long-term evolution under this treatment.
Keywords: Burosumab; FGF23; PHEX gene; X-linked hypophosphatemia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Fuente R., Gil-Peña H., Claramunt-Taberner D., Hernández-Frías O., Fernández-Iglesias Á., Hermida-Prado F., Anes-González G., Rubio-Aliaga I., Lopez J.M., Santos F. Marked Alterations in the Structure, Dynamics and Maturation of Growth Plate Likely Explain Growth Retardation and Bone Deformities of Young Hyp Mice. Bone. 2018;116:187–195. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2018.08.004. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

