Structural Insights and Development of LRRK2 Inhibitors for Parkinson's Disease in the Last Decade
- PMID: 36011337
- PMCID: PMC9408223
- DOI: 10.3390/genes13081426
Structural Insights and Development of LRRK2 Inhibitors for Parkinson's Disease in the Last Decade
Abstract
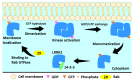
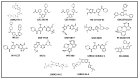
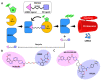
Parkinson's disease (PD) is the second most prevalent neurodegenerative disease, characterized by the specific loss of dopaminergic neurons in the midbrain. The pathophysiology of PD is likely caused by a variety of environmental and hereditary factors. Many single-gene mutations have been linked to this disease, but a significant number of studies indicate that mutations in the gene encoding leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) are a potential therapeutic target for both sporadic and familial forms of PD. Consequently, the identification of potential LRRK2 inhibitors has been the focus of drug discovery. Various investigations have been conducted in academic and industrial organizations to investigate the mechanism of LRRK2 in PD and further develop its inhibitors. This review summarizes the role of LRRK2 in PD and its structural details, especially the kinase domain. Furthermore, we reviewed in vitro and in vivo findings of selected inhibitors reported to date against wild-type and mutant versions of the LRRK2 kinase domain as well as the current trends researchers are employing in the development of LRRK2 inhibitors.
Keywords: G2019S mutation; LRRK2; Parkinson’s disease; kinase inhibitors; neurodegeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dopaminergic neurodegeneration induced by Parkinson's disease-linked G2019S LRRK2 is dependent on kinase and GTPase activity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Jul 21;117(29):17296-17307. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1922184117. Epub 2020 Jul 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32631998 Free PMC article.
-
Small molecule kinase inhibitors for LRRK2 and their application to Parkinson's disease models.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2012 Mar 21;3(3):151-60. doi: 10.1021/cn200117j. Epub 2012 Jan 18. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22860184 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Parkinson's Disease-Associated LRRK2 Hyperactive Kinase Mutant Disrupts Synaptic Vesicle Trafficking in Ventral Midbrain Neurons.J Neurosci. 2017 Nov 22;37(47):11366-11376. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0964-17.2017. Epub 2017 Oct 20. J Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29054882 Free PMC article.
-
Altered Development of Synapse Structure and Function in Striatum Caused by Parkinson's Disease-Linked LRRK2-G2019S Mutation.J Neurosci. 2016 Jul 6;36(27):7128-41. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3314-15.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27383589 Free PMC article.
-
Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 inhibitors: a review of recent patents (2011 - 2013).Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2014 Jul;24(7):745-57. doi: 10.1517/13543776.2014.907275. Epub 2014 Jun 11. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2014. PMID: 24918198 Review.
Cited by
-
Rotenone Induces a Neuropathological Phenotype in Cholinergic-like Neurons Resembling Parkinson's Disease Dementia (PDD).Neurotox Res. 2024 Jun 6;42(3):28. doi: 10.1007/s12640-024-00705-3. Neurotox Res. 2024. PMID: 38842585 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacology of LRRK2 with type I and II kinase inhibitors revealed by cryo-EM.Cell Discov. 2024 Jan 23;10(1):10. doi: 10.1038/s41421-023-00639-8. Cell Discov. 2024. PMID: 38263358 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocytes Differentiated from LRRK2-I1371V Parkinson's-Disease-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells Exhibit Similar Yield but Cell-Intrinsic Dysfunction in Glutamate Uptake and Metabolism, ATP Generation, and Nrf2-Mediated Glutathione Machinery.Cells. 2023 Jun 8;12(12):1592. doi: 10.3390/cells12121592. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37371062 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating the Expression and Prognostic Value of Genes Encoding Microtubule-Associated Proteins in Lung Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 25;23(23):14724. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314724. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36499051 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

