Study on the Spatial Interaction between Urban Economic and Ecological Environment-A Case Study of Wuhan City
- PMID: 36011657
- PMCID: PMC9407929
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph191610022
Study on the Spatial Interaction between Urban Economic and Ecological Environment-A Case Study of Wuhan City
Abstract
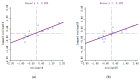
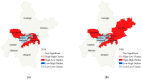
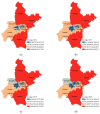
In order to study the interactive relationship between urban economic and ecological environment, taking Wuhan as an example, Landsat and MODIS remote sensing satellite data and social and economic data were fused with multisource data, and multidimensional indicators were selected to construct the comprehensive evaluation index system of urban economic and ecological environment. The weights were determined by combining subjective and objective methods. Then, the decoupling elasticity coefficient method and spatial autocorrelation model were used to evaluate the dynamic relationship and spatial relationship between economic development and ecological environment in Wuhan from 2014 to 2020. The results showed that there was an interaction between the urban economic and the ecological environment in Wuhan. The ecological level index had a spatial effect, the adjustment of industrial structure had a positive effect on the improvement of the ecological level, and the improvement of the ecological level was also helpful to promote economic development. The typical districts of Huangpi District, Xinzhou District, Jiangxia District, Hannan District, Caidian District, and Hongshan District had superior location and ecological advantages, as well as high development potential. Lastly, on the basis of the empirical analysis results, policy suggestions are made from four aspects: regional differentiated construction, green development, energy consumption, and wetland construction.
Keywords: decoupling elasticity coefficient method; ecological environment; multisource data fusion; spatial autocorrelation model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Study on volatile organic compounds emission of straw combustion and management countermeasure in Wuhan city].Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2013 Dec;34(12):4543-51. Huan Jing Ke Xue. 2013. PMID: 24640888 Chinese.
-
PM2.5-Related Health Economic Benefits Evaluation Based on Air Improvement Action Plan in Wuhan City, Middle China.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jan 18;17(2):620. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17020620. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 31963670 Free PMC article.
-
Empirical Study on the Influence of Urban Environmental Industrial Structure Optimization on Ecological Landscape Greening Construction.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Dec 15;19(24):16842. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192416842. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36554735 Free PMC article.
-
An Exploration of a Synthetic Construction Land Use Quality Evaluation Based on Economic-Social-Ecological Coupling Perspective: A Case Study in Major Chinese Cities.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 May 22;17(10):3663. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17103663. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32456116 Free PMC article.
-
Can the Adjustment and Renovation Policies of Old Industrial Cities Reduce Urban Carbon Emissions?-Empirical Analysis Based on Quasi-Natural Experiments.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 May 26;19(11):6453. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19116453. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35682040 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Li G., Fang C. Global mapping and estimation of ecosystem services values and gross domestic product: A spatially explicit integration of national ‘green GDP’accounting. Ecol. Indic. 2014;46:293–314. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2014.05.020. - DOI
-
- Shi T., Yang S., Zhang W., Zhou Q. Coupling coordination degree measurement and spatiotemporal heterogeneity between economic development and ecological environment—Empirical evidence from tropical and subtropical regions of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020;244:118739. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118739. - DOI
-
- Tao L.R.G. Construction and Application of the High-quality Development Index—Also on the High-quality Development of Northeast China’s Economy. J. Northeast. Univ. 2020;22:31–39. doi: 10.15936/j.cnki.1008-3758.2020.01.005. - DOI
-
- Sun Q. Urban Land Regulation and the Global Carbon Cycle: Its Ecological and Economic Effects. Open House Int. 2017;42:25–28. doi: 10.1108/OHI-03-2017-B0006. - DOI
-
- Du W., Yan H., Feng Z., Yang Y., Liu F. The supply-consumption relationship of ecological resources under ecological civilization construction in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021;172:105679. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.105679. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources