Rare Diseases: Needs and Impact for Patients and Families: A Cross-Sectional Study in the Valencian Region, Spain
- PMID: 36012000
- PMCID: PMC9408677
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph191610366
Rare Diseases: Needs and Impact for Patients and Families: A Cross-Sectional Study in the Valencian Region, Spain
Abstract
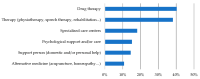
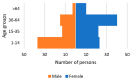
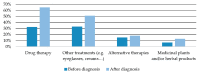
Families with rare diseases (RDs) have unmet needs that are often overlooked by health professionals. Describing these needs and the impact of the disease could improve their medical care. A total of 163 surveys were obtained from patients visiting primary care centres in the Valencian Region (Spain), during 2015-2017, with a confirmed or suspected diagnosis of RD. Of the 84.7% with a confirmed diagnosis, 50.4% had a diagnostic delay exceeding one year, and it was more prevalent among adults (62.2%). Families with paediatric patients were in a worse economic situation, with lower incomes and higher monthly disease-related expenses (€300 on average). These expenses were incurred by 66.5% of families and were mainly for medication (40.3%). Among them, 58.5% reported not being able to afford adjuvant therapies. The disease had an impact on 73.1% of families, especially on their routine and emotional state. Expenses, needs, and impacts were more frequent among families of patients with a history of hospitalisation or deterioration. Patients with delayed diagnosis had a higher consumption of drugs prior to diagnosis. People affected by RDs in the Valencian Region need therapies to improve their autonomy and emotional state. Health professionals should be aware of these needs.
Keywords: Spain; diagnostic delay; primary care; rare diseases; unmet needs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Diagnostic delay in rare diseases: data from the Spanish rare diseases patient registry.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022 Nov 17;17(1):418. doi: 10.1186/s13023-022-02530-3. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022. PMID: 36397119 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of strengths and weaknesses of the healthcare system for persons living with rare diseases in Catalonia (Spain), and recommendations to improve its comprehensive attention: the "acERca las enfermedades raras" project.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2025 Jan 29;20(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s13023-024-03518-x. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2025. PMID: 39875900 Free PMC article.
-
[Diagnostic delay in rare diseases: between fear and resilience].Gac Sanit. 2022 Dec 19;37:102272. doi: 10.1016/j.gaceta.2022.102272. eCollection 2023. Gac Sanit. 2022. PMID: 36542890 Spanish.
-
Shaping the Future of Rare Diseases after a Global Health Emergency: Organisational Points to Consider.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Nov 23;17(22):8694. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17228694. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 33238523 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Solidarity(-ies) in Rare Diseases Research.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1031:589-604. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-67144-4_31. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29214593 Review.
Cited by
-
Attitudes Toward Personal Health Data Sharing Among People Living With Sickle Cell Disorder, Exemplar for Study of Rare Disease Populations.J Patient Cent Res Rev. 2023 Apr 18;10(2):68-76. doi: 10.17294/2330-0698.2006. eCollection 2023 Spring. J Patient Cent Res Rev. 2023. PMID: 37091117 Free PMC article.
-
Capturing Real-World Rare Disease Patient Journeys: Are Current Methodologies Sufficient for Informed Healthcare Decisions?J Eval Clin Pract. 2025 Feb;31(1):e70010. doi: 10.1111/jep.70010. J Eval Clin Pract. 2025. PMID: 39960234 Free PMC article.
-
Criteria to evaluate unmet health-related needs of persons living with rare diseases and their caregivers: rapid literature review and stakeholder consultations.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2025 Jul 1;20(1):321. doi: 10.1186/s13023-025-03838-6. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2025. PMID: 40598354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psychosocial impact at the time of a rare disease diagnosis.PLoS One. 2023 Jul 28;18(7):e0288875. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0288875. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37506095 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology and Healthcare Utilization in Pediatric Multiple Sclerosis and Neuromyelitis Optica: A Nationwide Population-Based Study in South Korea (2016-2020).Children (Basel). 2024 May 5;11(5):553. doi: 10.3390/children11050553. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38790547 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wortmann J.K., Bremer A., Eich H., Wortmann H.K., Schuster A., Fühner J., Büntzel J., Muecke R., Prott F., Huebner J. Use of complementary and alternative medicine by patients with cancer: A cross-sectional study at different points of cancer care. Med. Oncol. 2016;33:78. doi: 10.1007/s12032-016-0790-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Thoene J., Crooks G.M. Report of the National Commission on Orphan Diseases. Public Health Service, Office of the Assistant Secretary of Health; Washington, DC, USA: 1989.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

