Multilayer Perceptron-Based Real-Time Intradialytic Hypotension Prediction Using Patient Baseline Information and Heart-Rate Variation
- PMID: 36012006
- PMCID: PMC9408052
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph191610373
Multilayer Perceptron-Based Real-Time Intradialytic Hypotension Prediction Using Patient Baseline Information and Heart-Rate Variation
Abstract
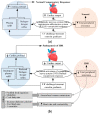
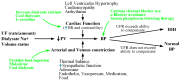
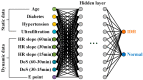
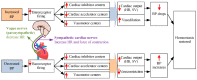
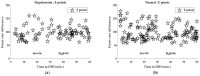
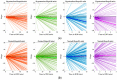
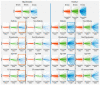
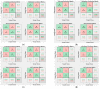
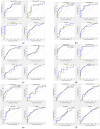
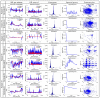
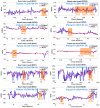
Intradialytic hypotension (IDH) is a common side effect that occurs during hemodialysis and poses a great risk for dialysis patients. Many studies have been conducted so far to predict IDH, but most of these could not be applied in real-time because they used only underlying patient information or static patient disease information. In this study, we propose a multilayer perceptron (MP)-based IDH prediction model using heart rate (HR) information corresponding to time-series information and static data of patients. This study aimed to validate whether HR differences and HR slope information affect real-time IDH prediction in patients undergoing hemodialysis. Clinical data were collected from 80 hemodialysis patients from 9 September to 17 October 2020, in the artificial kidney room at Yeungnam University Medical Center (YUMC), Daegu, South Korea. The patients typically underwent hemodialysis 12 times during this period, 1 to 2 h per session. Therefore, the HR difference and HR slope information within up to 1 h before IDH occurrence were used as time-series input data for the MP model. Among the MP models using the number and data length of different hidden layers, the model using 60 min of data before the occurrence of two layers and IDH showed maximum performance, with an accuracy of 81.5%, a true positive rate of 73.8%, and positive predictive value of 87.3%. This study aimed to predict IDH in real-time by continuously supplying HR information to MP models along with static data such as age, diabetes, hypertension, and ultrafiltration. The current MP model was implemented using relatively limited parameters; however, its performance may be further improved by adding additional parameters in the future, further enabling real-time IDH prediction to play a supporting role for medical staff.
Keywords: heart-rate; hemodialysis; intradialytic hypotension; multilayer perceptron; real-time.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Visual Indicator for Intradialytic Hypotension Prediction Using Variation and Compensation of Heart Rate.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Nov 26;14(23):2664. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14232664. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39682571 Free PMC article.
-
Real-time prediction of intradialytic hypotension using machine learning and cloud computing infrastructure.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2023 Jun 30;38(7):1761-1769. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfad070. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2023. PMID: 37055366 Free PMC article.
-
Personalized prediction of intradialytic hypotension in clinical practice: Development and evaluation of a novel AI dashboard incorporating risk factors from previous and current dialysis sessions.Int J Med Inform. 2024 Oct;190:105538. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2024.105538. Epub 2024 Jul 3. Int J Med Inform. 2024. PMID: 38968689
-
Intensive Hemodialysis and Treatment Complications and Tolerability.Am J Kidney Dis. 2016 Nov;68(5S1):S43-S50. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2016.05.021. Am J Kidney Dis. 2016. PMID: 27772642 Review.
-
The Prevalence of Intradialytic Hypotension in Patients on Conventional Hemodialysis: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis.Am J Nephrol. 2019;49(6):497-506. doi: 10.1159/000500877. Epub 2019 May 24. Am J Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31129661 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Classification of Blood Pressure Levels Based on Photoplethysmogram and Electrocardiogram Signals with a Concatenated Convolutional Neural Network.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Nov 21;12(11):2886. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12112886. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428946 Free PMC article.
-
Improving the Accuracy of Continuous Blood Glucose Measurement Using Personalized Calibration and Machine Learning.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Jul 27;13(15):2514. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13152514. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37568877 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of intradialytic hypotension by machine learning: A systematic review.J Nephrol. 2025 May 3. doi: 10.1007/s40620-025-02288-4. Online ahead of print. J Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40317447 Review.
-
Prediction models for intradialytic hypotension in hemodialysis patients: A protocol for systematic review and critical appraisal.PLoS One. 2024 Sep 9;19(9):e0310191. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0310191. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39250467 Free PMC article.
-
Visual Indicator for Intradialytic Hypotension Prediction Using Variation and Compensation of Heart Rate.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Nov 26;14(23):2664. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14232664. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39682571 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

