Molecular Biomarkers in Glioblastoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 36012105
- PMCID: PMC9408540
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23168835
Molecular Biomarkers in Glioblastoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Glioblastoma (GBM) is a highly aggressive cancer with poor prognosis that needs better treatment modalities. Moreover, there is a lack of reliable biomarkers to predict the response and outcome of current or newly designed therapies. While several molecular markers have been proposed as potential biomarkers for GBM, their uptake into clinical settings is slow and impeded by marker heterogeneity. Detailed assessment of prognostic and predictive value for biomarkers in well-defined clinical trial settings, if available, is scattered throughout the literature. Here we conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the prognostic and predictive significance of clinically relevant molecular biomarkers in GBM patients. Material and methods: A comprehensive literature search was conducted to retrieve publications from 3 databases (Pubmed, Cochrane and Embase) from January 2010 to December 2021, using specific terms. The combined hazard ratios (HR) and confidence intervals (95% CI) were used to evaluate the association of biomarkers with overall survival (OS) in GBM patients. Results: Twenty-six out of 1831 screened articles were included in this review. Nineteen articles were included in the meta-analyses, and 7 articles were quantitatively summarised. Fourteen studies with 1231 GBM patients showed a significant association of MGMT methylation with better OS with the pooled HR of 1.66 (95% CI 1.32−2.09, p < 0.0001, random effect). Five studies including 541 GBM patients analysed for the prognostic significance of IDH1 mutation showed significantly better OS in patients with IDH1 mutation with a pooled HR of 2.37 (95% CI 1.81−3.12; p < 0.00001]. Meta-analysis performed on 5 studies including 575 GBM patients presenting with either amplification or high expression of EGFR gene did not reveal any prognostic significance with a pooled HR of 1.31 (95% CI 0.96−1.79; p = 0.08). Conclusions: MGMT promoter methylation and IDH1 mutation are significantly associated with better OS in GBM patients. No significant associations were found between EGFR amplification or overexpression with OS.
Keywords: glioblastoma; meta-analysis; prognostic biomarkers; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
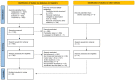

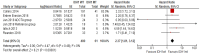

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

