IL11 Stimulates IL33 Expression and Proinflammatory Fibroblast Activation across Tissues
- PMID: 36012165
- PMCID: PMC9408968
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23168900
IL11 Stimulates IL33 Expression and Proinflammatory Fibroblast Activation across Tissues
Abstract
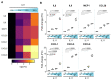
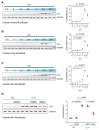
Interleukin 11 (IL11) is upregulated in inflammatory conditions, where it is mostly believed to have anti-inflammatory activity. However, recent studies suggest instead that IL11 promotes inflammation by activating fibroblasts. Here, we assessed whether IL11 is pro- or anti-inflammatory in fibroblasts. Primary cultures of human kidney, lung or skin fibroblasts were stimulated with IL11 that resulted in the transient phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) and the sustained activation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases (ERK). RNA sequencing over a time course of IL11 stimulation revealed a robust but short-lived transcriptional response that was enriched for gene set hallmarks of inflammation and characterized by the upregulation of SERPINB2, TNFRSF18, Interleukin 33 (IL33), CCL20, IL1RL1, CXCL3/5/8, ICAM1 and IL11 itself. IL33 was the most upregulated signaling factor (38-fold, p = 9.8 × 10-5), and IL1RL1, its cognate receptor, was similarly increased (18-fold, p = 1.1 × 10-34). In proteomic studies, IL11 triggered a proinflammatory secretome with the notable upregulation of IL8, IL6, MCP1, CCL20 and CXCL1/5/6, which are important chemotaxins for neutrophils, monocytes, and lymphocytes. IL11 induced IL33 expression across fibroblast types, and the inhibition of STAT3 but not of MEK/ERK prevented this. These data establish IL11 as pro-inflammatory with specific importance for priming the IL33 alarmin response in inflammatory fibroblasts across tissues.
Keywords: IL-11; IL-33; IL-6; fibroblasts; fibrosis; inflammation; interleukin; transcription; translation.
Conflict of interest statement
S.A.C is a co-inventor of patent applications WO/2018/109174 (IL11 ANTIBODIES) and WO/2018/109170 (IL11RA ANTIBODIES) and a co-founder and shareholder of Enleofen Bio PTE LTD.
Figures


Comment in
-
The inflammaging clock strikes IL-11!Immunity. 2024 Sep 10;57(9):2010-2012. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2024.08.010. Immunity. 2024. PMID: 39260354 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Paul S.R., Bennett F., Calvetti J.A., Kelleher K., Wood C.R., O’Hara R.M., Jr., Leary A.C., Sibley B., Clark S.C., Williams D.A., et al. Molecular Cloning of a cDNA Encoding Interleukin 11, a Stromal Cell-Derived Lymphopoietic and Hematopoietic Cytokine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 1990;87:7512–7516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7512. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu P., Lin B., Huang S., Meng J., Zhang F., Zhou M., Hei X., Ke Y., Yang H., Huang D. IL-11 Is Elevated and Drives the Profibrotic Phenotype Transition of Orbital Fibroblasts in Thyroid-Associated Ophthalmopathy. Front. Endocrinol. 2022;13:846106. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.846106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

