Immunofluorescent Evidence for Nuclear Localization of Aromatase in Astrocytes in the Rat Central Nervous System
- PMID: 36012212
- PMCID: PMC9408820
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23168946
Immunofluorescent Evidence for Nuclear Localization of Aromatase in Astrocytes in the Rat Central Nervous System
Abstract
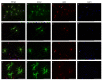
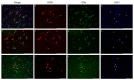
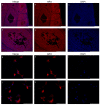
Estrogens regulate a variety of neuroendocrine, reproductive and also non-reproductive brain functions. Estradiol biosynthesis in the central nervous system (CNS) is catalyzed by the enzyme aromatase, which is expressed in several brain regions by neurons, astrocytes and microglia. In this study, we performed a complex fluorescent immunocytochemical analysis which revealed that aromatase is colocalized with the nuclear stain in glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) positive astrocytes in cell cultures. Confocal immunofluorescent Z-stack scanning analysis confirmed the colocalization of aromatase with the nuclear DAPI signal. Nuclear aromatase was also detectable in the S100β positive astrocyte subpopulation. When the nuclear aromatase signal was present, estrogen receptor alpha was also abundant in the nucleus. Immunostaining of frozen brain tissue sections showed that the nuclear colocalization of the enzyme in GFAP-positive astrocytes is also detectable in the adult rat brain. CD11b/c labelled microglial cells express aromatase, but the immunopositive signal was distributed only in the cytoplasm both in the ramified and amoeboid microglial forms. Immunostaining of rat ovarian tissue sections and human granulosa cells revealed that aromatase was present only in the cytoplasm. This novel observation suggests a new unique mechanism in astrocytes that may regulate certain CNS functions via estradiol production.
Keywords: aromatase; astrocyte; central nervous system; estrogen; estrogen receptor alpha; microglia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Astrocyte-Derived Estrogen Regulates Reactive Astrogliosis and is Neuroprotective following Ischemic Brain Injury.J Neurosci. 2020 Dec 9;40(50):9751-9771. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0888-20.2020. Epub 2020 Nov 6. J Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33158962 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of primary human fetal dissociated central nervous system cultures with an emphasis on microglia.Lab Invest. 1992 Oct;67(4):465-76. Lab Invest. 1992. PMID: 1359193
-
Aromatase expression by astrocytes after brain injury: implications for local estrogen formation in brain repair.Neuroscience. 1999 Mar;89(2):567-78. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(98)00340-6. Neuroscience. 1999. PMID: 10077336
-
Effects of testosterone and its metabolites on aromatase-immunoreactive cells in the quail brain: relationship with the activation of male reproductive behavior.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1996 Jan;56(1-6 Spec No):185-200. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(95)00236-7. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 8603040 Review.
-
Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and the astrocyte intermediate filament system in diseases of the central nervous system.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2015 Feb;32:121-30. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2015.02.004. Epub 2015 Mar 2. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25726916 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of estrogen in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis and therapeutic potential in women.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Apr;480(4):1983-1998. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-05071-4. Epub 2024 Aug 1. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 39088186 Review.
-
Brain-Derived Estrogen Regulates Neurogenesis, Learning and Memory with Aging in Female Rats.Biology (Basel). 2023 May 23;12(6):760. doi: 10.3390/biology12060760. Biology (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37372046 Free PMC article.
-
Testosterone Inhibits Secretion of the Pro-Inflammatory Chemokine CXCL1 from Astrocytes.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Mar 6;46(3):2105-2118. doi: 10.3390/cimb46030135. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38534751 Free PMC article.
-
Modular molecular design of polymerized pro-estrogen materials enables controlled astrocyte response.J Mater Chem B. 2025 Jun 4;13(22):6376-6392. doi: 10.1039/d5tb00285k. J Mater Chem B. 2025. PMID: 40351000 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Krentzel A.A., Willett J.A., Johnson A.G., Meitzen J. Estrogen receptor alpha, G-protein coupled estrogen receptor 1, and aromatase: Developmental, sex, and region-specific differences across the rat caudate-putamen, nucleus accumbens core and shell. J. Comp. Neurol. 2020;529:786–801. doi: 10.1002/cne.24978. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

