(-)-Epicatechin Is a Biased Ligand of Apelin Receptor
- PMID: 36012227
- PMCID: PMC9409145
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23168962
(-)-Epicatechin Is a Biased Ligand of Apelin Receptor
Abstract
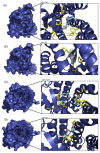
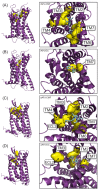
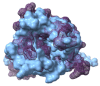
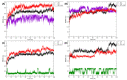
(-)-Epicatechin (EC) is part of a large family of biomolecules called flavonoids and is widely distributed in the plant kingdom. Several studies have shown the beneficial effects of EC consumption. Many of these reported effects are exerted by activating the signaling pathways associated with the activation of two specific receptors: the G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER), a transmembrane receptor, and the pregnane X receptor (PXR), which is a nuclear receptor. However, the effects of EC are so diverse that these two receptors cannot describe the complete phenomenon. The apelin receptor or APLNR is classified within the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) family, and is capable of activating the G protein canonical pathways and the β-arrestin transducer, which participates in the phenomenon of receptor desensitization and internalization. β-arrestin gained interest in selective pharmacology and mediators of the so-called "biased agonism". With molecular dynamics (MD) and in vitro assays, we demonstrate how EC can recruit the β-arrestin in the active conformation of the APLN receptor acting as a biased agonist.
Keywords: (-)-epicatechin; APLNR; bias ligand; molecular dynamics; β-arrestin.
Conflict of interest statement
F.V. is the founder and stockholder of Epirium Inc., and G.C. is a stockholder of Epirium Inc. The rest of the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A Systematic Approach to Identify Biased Agonists of the Apelin Receptor through High-Throughput Screening.SLAS Discov. 2017 Aug;22(7):867-878. doi: 10.1177/2472555217699158. Epub 2017 Mar 17. SLAS Discov. 2017. PMID: 28314120
-
GPCR structure and function relationship: identification of a biased apelin receptor mutant.Biochem J. 2018 Dec 6;475(23):3813-3826. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20180740. Biochem J. 2018. PMID: 30409826
-
Apelin-36-[L28A] and Apelin-36-[L28C(30kDa-PEG)] peptides that improve diet induced obesity are G protein biased ligands at the apelin receptor.Peptides. 2019 Nov;121:170139. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2019.170139. Epub 2019 Aug 28. Peptides. 2019. PMID: 31472173 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating structural and molecular mechanisms of β-arrestin-biased agonism at GPCRs via MS-based proteomics.Cell Signal. 2018 Jan;41:56-64. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2017.09.013. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Cell Signal. 2018. PMID: 28939107 Review.
-
Allosteric coupling and biased agonism in G protein-coupled receptors.FEBS J. 2021 Apr;288(8):2513-2528. doi: 10.1111/febs.15783. Epub 2021 Mar 5. FEBS J. 2021. PMID: 33621418 Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic Effects of Apelin on Cardiovascular Regulation and Angiotensin II-Induced Hypertension.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Apr 17;16(4):600. doi: 10.3390/ph16040600. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37111357 Free PMC article.
-
Positive Effects of (+)-Epicatechin on Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury Recovery.Biomolecules. 2025 Jun 14;15(6):869. doi: 10.3390/biom15060869. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40563509 Free PMC article.
-
Role of GPCR Signaling in Anthracycline-Induced Cardiotoxicity.Cells. 2025 Jan 22;14(3):169. doi: 10.3390/cells14030169. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39936961 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Taub P.R., Ramirez-Sanchez I., Ciaraldi T.P., Gonzalez-Basurto S., Coral-Vazquez R., Perkins G., Hogan M., Maisel A.S., Henry R.R., Ceballos G., et al. Perturbations in skeletal muscle sarcomere structure in patients with heart failure and Type 2 diabetes: Restorative effects of (-)-epicatechinrich cocoa. Clin. Sci. 2013;125:383–389. doi: 10.1042/CS20130023. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ramirez-Sanchez I., Taub P.R., Ciaraldi T.P., Nogueira L., Coe T., Perkins G., Hogan M., Maisel A.S., Henry R.R., Ceballos G., et al. (-)-Epicatechin rich cocoa mediated modulation of oxidative stress regulators in skeletal muscle of heart failure and type 2 diabetes patients. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013;168:3982–3990. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.06.089. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gutiérrez-Salmeán G., Ortiz-Vilchis P., Vacaseydel C.M., Garduño-Siciliano L., Chamorro-Cevallos G., Meaney E., Villafaña S., Villarreal F., Ceballos G., Ramírez-Sánchez I. Effects of (-)-epicatechin on a diet-induced rat model of cardiometabolic risk factors. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2014;728:24–30. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.01.053. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Moreno-Ulloa A., Miranda-Cervantes A., Licea-Navarro A., Mansour C., Beltrán-Partida E., Donis-Maturano L., de la Herrán H.C.D., Villarreal F., Álvarez-Delgado C. (-)-Epicatechin Stimulates Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Cell Growth in C2C12 Myotubes via the G-Protein Coupled Estrogen Receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018;822:95. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.01.014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

