Antitumor Effects of a New Retinoate of the Fungal Cytotoxin Illudin M in Brain Tumor Models
- PMID: 36012321
- PMCID: PMC9408991
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23169056
Antitumor Effects of a New Retinoate of the Fungal Cytotoxin Illudin M in Brain Tumor Models
Abstract
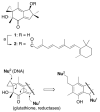
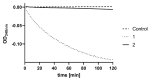
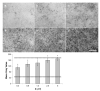
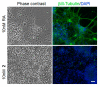
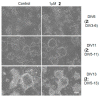
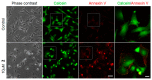
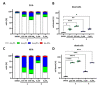
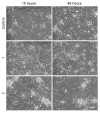
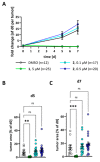
While the fungal metabolite illudin M (1) is indiscriminately cytotoxic in cancer and non-malignant cells, its retinoate 2 showed a greater selectivity for the former, especially in a cerebral context. Illudin M killed malignant glioma cells as well as primary neurons and astrocytes at similarly low concentrations and destroyed their microtubule and glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) networks. In contrast, the ester 2 was distinctly more cytotoxic in highly dedifferentiated U87 glioma cells than in neurons, which were even stimulated to enhanced growth. This was also observed in co-cultures of neurons with U87 cells where conjugate 2 eventually killed them by induction of differentiation based on the activation of nuclear receptors, which bind to retinoid-responsive elements (RARE). Hence, illudin M retinoate 2 appears to be a promising drug candidate.
Keywords: anticancer agents; brain tumors; illudin M; neuronal cells; retinoic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

