Gene Network Analysis of the Transcriptome Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Interacting MicroRNAs in COVID-19 Disease
- PMID: 36012503
- PMCID: PMC9409149
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23169239
Gene Network Analysis of the Transcriptome Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Interacting MicroRNAs in COVID-19 Disease
Abstract
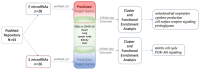
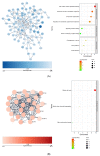
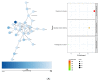
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), as of June 2022, over 536 million confirmed COVID-19 disease cases and over 6.3 million deaths had been globally reported. COVID-19 is a multiorgan disease involving multiple intricated pathological mechanisms translated into clinical, biochemical, and molecular changes, including microRNAs. MicroRNAs are essential post-transcriptional regulators of gene expression, being involved in the modulation of most biological processes. In this study, we characterized the biological impact of SARS-CoV-2 interacting microRNAs differentially expressed in COVID-19 disease by analyzing their impact on five distinct tissue transcriptomes. To this end, we identified the microRNAs' predicted targets within the list of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in tissues affected by high loads of SARS-CoV-2 virus. Next, we submitted the tissue-specific lists of the predicted microRNA-targeted DEGs to gene network functional enrichment analysis. Our data show that the upregulated microRNAs control processes such as mitochondrial respiration and cytokine and cell surface receptor signaling pathways in the heart, lymph node, and kidneys. In contrast, downregulated microRNAs are primarily involved in processes related to the mitotic cell cycle in the heart, lung, and kidneys. Our study provides the first exploratory, systematic look into the biological impact of the microRNAs associated with COVID-19, providing a new perspective for understanding its multiorgan physiopathology.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; microRNA; network analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Role of SARS-CoV-2 in Altering the RNA-Binding Protein and miRNA-Directed Post-Transcriptional Regulatory Networks in Humans.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 25;21(19):7090. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197090. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32993015 Free PMC article.
-
A new insight into sex-specific non-coding RNAs and networks in response to SARS-CoV-2.Infect Genet Evol. 2022 Jan;97:105195. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2021.105195. Epub 2021 Dec 23. Infect Genet Evol. 2022. PMID: 34954105 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV infection crosstalk with human host cell noncoding-RNA machinery: An in-silico approach.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Oct;130:110548. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110548. Epub 2020 Jul 28. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 33475497 Free PMC article.
-
The role of microRNAs in modulating SARS-CoV-2 infection in human cells: a systematic review.Infect Genet Evol. 2021 Jul;91:104832. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2021.104832. Epub 2021 Apr 1. Infect Genet Evol. 2021. PMID: 33812037 Free PMC article.
-
[MicroRNAs as the Potential Regulators of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Modifiers of the COVID-19 Clinical Features].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2022 Jan-Feb;56(1):35-54. doi: 10.31857/S0026898422010049. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2022. PMID: 35082257 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
COVID-19-Related Age Profiles for SARS-CoV-2 Variants in England and Wales and States of the USA (2020 to 2022): Impact on All-Cause Mortality.Infect Dis Rep. 2023 Oct 8;15(5):600-634. doi: 10.3390/idr15050058. Infect Dis Rep. 2023. PMID: 37888139 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding RNAs Emerging as Drugs or Drug Targets: Their Chemical Modification, Bio-Conjugation and Intracellular Regulation.Molecules. 2022 Oct 9;27(19):6717. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196717. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36235253 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoding HiPSC-CM's Response to SARS-CoV-2: mapping the molecular landscape of cardiac injury.BMC Genomics. 2024 Mar 12;25(1):271. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10194-5. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38475718 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating miRNAs in the Plasma of Post-COVID-19 Patients with Typical Recovery and Those with Long-COVID Symptoms: Regulation of Immune Response-Associated Pathways.Noncoding RNA. 2024 Sep 2;10(5):48. doi: 10.3390/ncrna10050048. Noncoding RNA. 2024. PMID: 39311385 Free PMC article.
-
Whole transcriptome sequencing for revealing the pathogenesis of sporotrichosis caused by Sporothrix globosa.Sci Rep. 2024 Jan 3;14(1):359. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-50728-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38172590 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. [(accessed on 25 June 2022)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

