Expression of MicroRNAs in Sepsis-Related Organ Dysfunction: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 36012630
- PMCID: PMC9409129
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23169354
Expression of MicroRNAs in Sepsis-Related Organ Dysfunction: A Systematic Review
Abstract
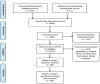
Sepsis is a critical condition characterized by increased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines and proliferating cells such as neutrophils and macrophages in response to microbial pathogens. Such processes lead to an abnormal inflammatory response and multi-organ failure. MicroRNAs (miRNA) are single-stranded non-coding RNAs with the function of gene regulation. This means that miRNAs are involved in multiple intracellular pathways and thus contribute to or inhibit inflammation. As a result, their variable expression in different tissues and organs may play a key role in regulating the pathophysiological events of sepsis. Thanks to this property, miRNAs may serve as potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in such life-threatening events. In this narrative review, we collect the results of recent studies on the expression of miRNAs in heart, blood, lung, liver, brain, and kidney during sepsis and the molecular processes in which they are involved. In reviewing the literature, we find at least 122 miRNAs and signaling pathways involved in sepsis-related organ dysfunction. This may help clinicians to detect, prevent, and treat sepsis-related organ failures early, although further studies are needed to deepen the knowledge of their potential contribution.
Keywords: blood; brain; heart; kidney; liver; lungs; miRNA; microRNA; multiple organ dysfunction; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Singer M., Deutschman C.S., Seymour C.W., Shankar-Hari M., Annane D., Bauer M., Bellomo R., Bernard G.R., Chiche J.-D., Coopersmith C.M., et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3) JAMA. 2016;315:801–810. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Evans L., Rhodes A., Alhazzani W., Antonelli M., Coopersmith C.M., French C., Machado F.R., Mcintyre L., Ostermann M., Prescott H.C., et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Intensiv. Care Med. 2021;47:1181–1247. doi: 10.1007/s00134-021-06506-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fleischmann-Struzek C., Mellhammar L., Rose N., Cassini A., Rudd K.E., Schlattmann P., Allegranzi B., Reinhart K. Incidence and mortality of hospital- and ICU-treated sepsis: Results from an updated and expanded systematic review and meta-analysis. Intensiv. Care Med. 2020;46:1552–1562. doi: 10.1007/s00134-020-06151-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials