Management of High-Risk Hypercholesterolemic Patients and PCSK9 Inhibitors Reimbursement Policies: Data from a Cohort of Italian Hypercholesterolemic Outpatients
- PMID: 36012937
- PMCID: PMC9410302
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11164701
Management of High-Risk Hypercholesterolemic Patients and PCSK9 Inhibitors Reimbursement Policies: Data from a Cohort of Italian Hypercholesterolemic Outpatients
Abstract
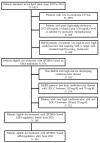
Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors are effective and safe lipid-lowering treatments (LLT). The primary endpoint of the study was to assess the prevalence of patients eligible for treatment with PCSK9 inhibitors in a real-life clinical setting in Italy before and after the recent enlargement of reimbursement criteria. For this study, we consecutively considered the clinical record forms of 6231 outpatients consecutively admitted at the Lipid Clinic of the University Hospital of Bologna (Italy). Patients were stratified according to whether they were allowed or not allowed to access to treatment with PCSK9 inhibitors based on national prescription criteria and reimbursement rules issued by the Italian Medicines Agency (AIFA). According to the indications of the European Medicines Agency (EMA), 986 patients were candidates to treatment with PCSK9 inhibitors. However, following the prescription criteria issued by AIFA, only 180 patients were allowed to access to PCSK9 inhibitors before reimbursement criteria enlargement while 322 (+14.4%) with the current ones. Based on our observations, low-cost tailored therapeutic interventions for individual patients can significantly reduce the number of patients potentially needing treatment with PCSK9 inhibitors among those who are not allowed to access to the treatment. The application of enlarged reimbursement criteria for PCSK9 inhibitors could mildly improve possibility to adequately manage high-risk hypercholesterolemic subjects in the setting of an outpatient lipid clinic.
Keywords: LDL-C; LDL-C goal; PCSK9 inhibitors; cardiovascular risk; hypercholesterolemia; tailored medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Bonaca M.P., Nault P., Giugliano R.P., Keech A.C., Pineda A.L., Kanevsky E., Kuder J., Murphy S.A., Jukema J.W., Lewis B.S., et al. Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Lowering with Evolocumab and Outcomes in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease: Insights from the FOURIER Trial (Further Cardiovascular Outcomes Research with PCSK9 Inhibition in Subjects with Elevated Risk) Circulation. 2018;137:338–350. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.032235. - DOI - PubMed
-
- [(accessed on 9 June 2022)]. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/product-information/repatha-epar-....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous