Subretinal Injection Techniques for Retinal Disease: A Review
- PMID: 36012955
- PMCID: PMC9409835
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11164717
Subretinal Injection Techniques for Retinal Disease: A Review
Abstract
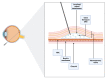
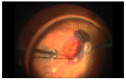
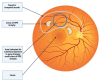
Inherited retinal dystrophies (IRDs) affect an estimated 1 in every 2000 people, this corresponding to nearly 2 million cases worldwide. Currently, 270 genes have been associated with IRDs, most of them altering the function of photoreceptors and retinal pigment epithelium. Gene therapy has been proposed as a potential tool for improving visual function in these patients. Clinical trials in animal models and humans have been successful in various types of IRDs. Recently, voretigene neparvovec (Luxturna®) has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of biallelic mutations in the RPE65 gene. The current state of the art in gene therapy involves the delivery of various types of viral vectors into the subretinal space to effectively transduce diseased photoreceptors and retinal pigment epithelium. For this, subretinal injection is becoming increasingly popular among researchers and clinicians. To date, several approaches for subretinal injection have been described in the scientific literature, all of them effective in accessing the subretinal space. The growth and development of gene therapy give rise to the need for a standardized procedure for subretinal injection that ensures the efficacy and safety of this new approach to drug delivery. The goal of this review is to offer an insight into the current subretinal injection techniques and understand the key factors in the success of this procedure.
Keywords: retinal gene therapy; subretinal injection; subretinal injection technique; vitreoretinal surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
A.L.-L. and J.R.-E. are employees at Miramoon Pharma. Both authors (A.L.-L. and J.R.-E.) declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article and with any of the other authors.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Voretigene Neparvovec: A Review in RPE65 Mutation-Associated Inherited Retinal Dystrophy.Mol Diagn Ther. 2020 Aug;24(4):487-495. doi: 10.1007/s40291-020-00475-6. Mol Diagn Ther. 2020. PMID: 32535767 Review.
-
Gene therapy for inherited retinal diseases: progress and possibilities.Clin Exp Optom. 2021 May;104(4):444-454. doi: 10.1080/08164622.2021.1880863. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Clin Exp Optom. 2021. PMID: 33689657 Review.
-
Voretigene Neparvovec: An Emerging Gene Therapy for the Treatment of Inherited Blindness.2018 Mar 1. In: CADTH Issues in Emerging Health Technologies. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2016–2021. 169. 2018 Mar 1. In: CADTH Issues in Emerging Health Technologies. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health; 2016–2021. 169. PMID: 30855774 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Voretigene Neparvovec in Retinal Diseases: A Review of the Current Clinical Evidence.Clin Ophthalmol. 2020 Nov 13;14:3855-3869. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S231804. eCollection 2020. Clin Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 33223822 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Subretinal Injection of Voretigene Neparvovec-rzyl in a Patient With RPE65-Associated Leber's Congenital Amaurosis.Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging Retina. 2019 Oct 1;50(10):661-663. doi: 10.3928/23258160-20191009-01. Ophthalmic Surg Lasers Imaging Retina. 2019. PMID: 31671202
Cited by
-
Pharmacotherapy and Nutritional Supplements for Neovascular Eye Diseases.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Jul 20;59(7):1334. doi: 10.3390/medicina59071334. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37512145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Co-delivery of antioxidants and siRNA-VEGF: promising treatment for age-related macular degeneration.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025 Jul;15(7):2272-2300. doi: 10.1007/s13346-024-01772-x. Epub 2025 Jan 3. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 39751765 Review.
-
Advances in Regenerative Medicine, Cell Therapy, and 3D Bioprinting for Glaucoma and Retinal Diseases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025;1483:115-139. doi: 10.1007/5584_2025_854. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2025. PMID: 40131702 Review.
-
Advances and Challenges in Gene Therapy for Inherited Retinal Dystrophies: A Comprehensive Review.Cureus. 2024 Sep 22;16(9):e69895. doi: 10.7759/cureus.69895. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39439625 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulatable Complement Inhibition of the Alternative Pathway Mitigates Wet Age-Related Macular Degeneration Pathology in a Mouse Model.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2023 Jul 3;12(7):17. doi: 10.1167/tvst.12.7.17. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2023. PMID: 37462980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Romero-Aroca P., Méndez-Marin I., Salvat-Serra M., Fernández-Ballart J., Almena-Garcia M., Reyes-Torres J. Results at seven years after the use of intracamerular cefazolin as an endophthalmitis prophylaxis in cataract surgery. BMC Ophthalmol. 2012;12:2. doi: 10.1186/1471-2415-12-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Prasad A.G., Schadlu R., Apte R.S. Intravitreal pharmacotherapy: Applications in retinal disease. Compr. Ophthalmol. Updat. 2007;8:259–269. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

