Lung Transplant for ARDS after COVID-19: Long-Term Outcomes and Considerations about Detrimental Issues
- PMID: 36012993
- PMCID: PMC9409702
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm11164754
Lung Transplant for ARDS after COVID-19: Long-Term Outcomes and Considerations about Detrimental Issues
Abstract
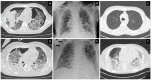
During the first outbreak of COVID-19 in Italy, based on the only few cases reported from a Chinese centre at the time, we performed lung transplantation in two patients with irreversible acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) after COVID-19 at our centre. After two years, we report the outcomes of these cases and some considerations. The first patient, an 18-year-old male, is in excellent conditions twenty-four months after surgery. The second patient was a 48-year-old man; his airways were colonized by carbapenemase-producing klebsiella pneumoniae at the time of lung transplantation, and he had previously suffered from delirium and hallucinations in the intensive care unit. His postoperative clinical course was complicated by dysexecutive behaviour and then septic shock; he died 62 days after surgery. The recently reported experience of different transplantation centres has led to the inclusion of irreversible acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) after COVID-19 among the indications for lung transplantation in carefully selected patients. Our results confirm the feasibility and the good long-term outcomes of lung transplantation for COVID-19-associated ARDS. Nonetheless, our experience corroborates the need for careful recipient selection: special attention must be paid to the single-organ dysfunction principle, the evaluation of any neuro-psychiatric disorder, and MDR germs colonization, before listing.
Keywords: ARDS; COVID-19; lung transplantation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chen J.Y., Qiao K., Liu F., Wu B., Xu X., Jiao G.Q., Lu R.G., Li H.X., Zhao J., Huang J., et al. Lung transplantation as therapeutic option in acute respiratory distress syndrome for coronavirus disease 2019-related pulmonary fibrosis. Chin. Med. J. 2020;133:1390–1396. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000839. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bharat A., Machuca T.N., Querrey M., Kurihara C., Garza-Castillon R., Jr., Kim S., Manerikar A., Pelaez A., Pipkin M., Shahmohammadi A., et al. Early outcomes after lung transplantation for severe COVID-19: A series of the first consecutive cases from four countries. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021;9:487–497. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00077-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kurihara C., Manerikar A., Querrey M., Felicelli C., Yeldandi A., Garza-Castillon R., Jr., Lung K., Kim S., Ho B., Tomic R., et al. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients With COVID-19-Associated Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Who Underwent Lung Transplant. JAMA. 2022;327:652–661. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.0204. - DOI - PMC - PubMed

