Global Challenges to Public Health Care Systems during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Review of Pandemic Measures and Problems
- PMID: 36013244
- PMCID: PMC9409667
- DOI: 10.3390/jpm12081295
Global Challenges to Public Health Care Systems during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Review of Pandemic Measures and Problems
Abstract
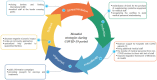
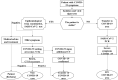
Beginning in December 2019, the world faced a critical new public health stressor with the emergence of SARS-CoV-2. Its spread was extraordinarily rapid, and in a matter of weeks countries across the world were affected, notably in their ability to manage health care needs. While many sectors of public structures were impacted by the pandemic, it particularly highlighted shortcomings in medical care infrastructures around the world that underscored the need to reorganize medical systems, as they were vastly unprepared and ill-equipped to manage a pandemic and simultaneously provide general and specialized medical care. This paper presents modalities in approaches to the pandemic by various countries, and the triaged reorganization of medical sections not considered first-line in the pandemic that was in many cases transformed into wards for treating COVID-19 cases. As new viruses and structural variants emerge, it is important to find solutions to streamline medical care in hospitals, which includes the expansion of digital network medicine (i.e., telemedicine and mobile health apps) for patients to continue to receive appropriate care without risking exposure to contagions. Mobile health app development continues to evolve with specialized diagnostics capabilities via external attachments that can provide rapid information sharing between patients and care providers while eliminating the need for office visits. Telemedicine, still in the early stages of adoption, especially in the developing world, can ensure access to medical information and contact with care providers, with the potential to release emergency rooms from excessive cases, and offer multidisciplinary access for patients and care providers that can also be a means to avoid contact during a pandemic. As this pandemic illustrated, an overhaul to streamline health care is essential, and a move towards greater use of mobile health and telemedicine will greatly benefit public health to control the spread of new variants and future outbreaks.
Keywords: medical system reorganization; prevention; protection; telemedicine; workflow.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Combating COVID-19 Pandemic: The Best Management Practices of a Designated Hospital in Southern Philippines. [(accessed on 31 October 2021)]. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/344468342_Combating_COVID-19_Pa....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous