Microbial Diversity and Community Composition of Duodenum Microbiota of High and Low Egg-Yielding Taihang Chickens Identified Using 16S rRNA Amplicon Sequencing
- PMID: 36013441
- PMCID: PMC9409686
- DOI: 10.3390/life12081262
Microbial Diversity and Community Composition of Duodenum Microbiota of High and Low Egg-Yielding Taihang Chickens Identified Using 16S rRNA Amplicon Sequencing
Abstract
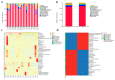
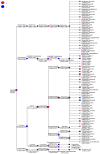
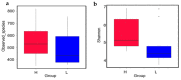
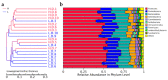
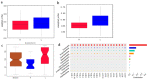
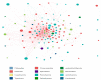
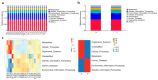
The duodenum is an important digestive organ for poultry and houses a variety of microbes that help chickens to enhance nutrient absorption and improve production. To evaluate the characteristic of gut microbiome, duodenum content samples from 42-week-old native Taihang chickens with high (H) and low (L) egg-yielding were collected for 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing analysis. Consequently, 1,361,341 sequences were clustered into 2055 OTUs, with percentages of affiliation of 96.50 and 57.30% at phylum and genus levels. Firmicutes, Proteobacteria, Cyanobacteria and Bacteroidetes were the dominant phylum, with a lower ratio of Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes in H group than in L group (p < 0.05). At genus level, overrepresentation of Bacteroides, Faecalibacterim, and Enterococcus and underrepresentation of Romboutsia were found in H group. No significant difference in overall diversity of microbiota was observed between two groups. LEFSe analysis revealed Enterococcus was significantly enriched in H group. Importantly, Enterococcus and Lactobacillus were negatively correlated. Functional prediction analysis showed the proportion of microbiota involved in the metabolism process was the highest and enriched in H group. Differences in microbiota composition between the two groups, which may be related to intestinal function difference, also provide promising biomarkers for improving laying hen production.
Keywords: Taihang chicken; bacterial diversity; egg-laying performance; function prediction; high-throughput sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

