Characterization of Bacterial Communities from the Surface and Adjacent Bottom Layers of Water in the Billings Reservoir
- PMID: 36013459
- PMCID: PMC9409723
- DOI: 10.3390/life12081280
Characterization of Bacterial Communities from the Surface and Adjacent Bottom Layers of Water in the Billings Reservoir
Abstract
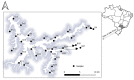
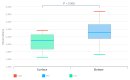
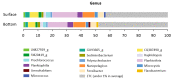
Here, we describe the bacterial diversity and physicochemical properties in freshwater samples from the surface and bottom layers of the Billings Reservoir, the largest open-air storage ecosystem in the São Paulo (Brazil) metropolitan area. Forty-four samples (22 from the surface and 22 from the bottom layers) were characterized based on 16S rRNA gene analysis using Illumina MiSeq. Taxonomical composition revealed an abundance of the Cyanobacteria phylum, followed by Proteobacteria, which were grouped into 1903 and 2689 different genera in the surface and the deep-water layers, respectively. Chroobacteria, Actinobacteria, Betaproteobacteria, and Alphaproteobacteria were the most dominant classes. The Shannon diversity index was in the range of 2.3-5.39 and 4.04-6.86 in the surface and bottom layers, respectively. Flavobacterium was the most predominant pathogenic genus. Temperature and phosphorus concentrations were among the most influential factors in shaping the microbial communities of both layers. Predictive functional analysis suggests that the reservoir is enriched in motility genes involved in flagellar assembly. The overall results provide new information on the diversity composition, ecological function, and health risks of the bacterial community detected in the Billings freshwater reservoir. The broad bacterial diversity indicates that the bacterioplankton communities in the reservoir were involved in multiple essential environmental processes.
Keywords: 16S rRNA gene; Illumina MiSeq; bacterial composition; bacterial diversity; billings reservoir.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Connor R. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2015: Water for a Sustainable World. United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization; Paris, France: 2015. WWAP-United Nations World Water Assessment Programme.
-
- Mishra A.K.E., editor. Application of Nanotechnology in Water Research. John Wiley & Sons; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2014.
-
- Shi X., Ma W., Li X., Cheng Y., Huang T. Typical Reservoir Pollution Source Analysis. In: Huang T., editor. Water Pollution and Water Quality Control of Selected Chinese Reservoir Basins. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2016. pp. 95–130.
-
- Gonçalves S.P., Lucheta F., Souza V.K.D., Terra N.R. The influence of xenobiotics in river sediment on the reproduction and survival of Daphnia magna, 1820, Straus. Acta Limnol. Bras. 2012;24:220–234. doi: 10.1590/S2179-975X2012005000040. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

