Identification and Characterization of Bacteria-Derived Antibiotics for the Biological Control of Pea Aphanomyces Root Rot
- PMID: 36014014
- PMCID: PMC9416638
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms10081596
Identification and Characterization of Bacteria-Derived Antibiotics for the Biological Control of Pea Aphanomyces Root Rot
Abstract
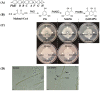
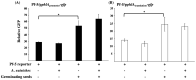
Antibiosis has been proposed to contribute to the beneficial bacteria-mediated biocontrol against pea Aphanomyces root rot caused by the oomycete pathogen Aphanomyces euteiches. However, the antibiotics required for disease suppression remain unknown. In this study, we found that the wild type strains of Pseudomonas protegens Pf-5 and Pseudomonas fluorescens 2P24, but not their mutants that lack 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol, strongly inhibited A. euteiches on culture plates. Purified 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol compound caused extensive hyphal branching and stunted hyphal growth of A. euteiches. Using a GFP-based transcriptional reporter assay, we found that expression of the 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol biosynthesis gene phlAPf-5 is activated by germinating pea seeds. The 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol producing Pf-5 derivative, but not its 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol non-producing mutant, reduced disease severity caused by A. euteiches on pea plants in greenhouse conditions. This is the first report that 2,4-diacetylphloroglucinol produced by strains of Pseudomonas species plays an important role in the biocontrol of pea Aphanomyces root rot.
Keywords: 2,4-DAPG; Aphanomyces euteiches; Pseudomonas spp.; antibiotics; biocontrol.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- O’Brien P.A. Biological control of plant diseases. Australas. Plant Pathol. 2017;46:293–304. doi: 10.1007/s13313-017-0481-4. - DOI
-
- Wu L., Chang K.-F., Hwang S.-F., Conner R., Fredua-Agyeman R., Feindel D., Strelkov S.E. Evaluation of host resistance and fungicide application as tools for the management of root rot of field pea caused by Aphanomyces euteiches. Crop J. 2019;7:38–48. doi: 10.1016/j.cj.2018.07.005. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

