Loss of rpoE Encoding the δ-Factor of RNA Polymerase Impacts Pathophysiology of the Streptococcus pyogenes M1T1 Strain 5448
- PMID: 36014103
- PMCID: PMC9412562
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms10081686
Loss of rpoE Encoding the δ-Factor of RNA Polymerase Impacts Pathophysiology of the Streptococcus pyogenes M1T1 Strain 5448
Abstract
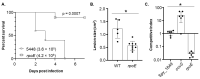
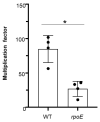
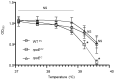
Streptococcus pyogenes, also known as the Group A Streptococcus (GAS), is a Gram-positive bacterial pathogen of major clinical significance. Despite remaining relatively susceptible to conventional antimicrobial therapeutics, GAS still causes millions of infections and hundreds of thousands of deaths each year worldwide. Thus, a need for prophylactic and therapeutic interventions for GAS is in great demand. In this study, we investigated the importance of the gene encoding the delta (δ) subunit of the GAS RNA polymerase, rpoE, for its impact on virulence during skin and soft-tissue infection. A defined 5448 mutant with an insertionally-inactivated rpoE gene was defective for survival in whole human blood and was attenuated for both disseminated lethality and lesion size upon mono-culture infection in mouse soft tissue. Furthermore, the mutant had reduced competitive fitness when co-infected with wild type (WT) 5448 in the mouse model. We were unable to attribute this attenuation to any observable growth defect, although colony size and the ability to grow at higher temperatures were both affected when grown with nutrient-rich THY media. RNA-seq of GAS grown in THY to late log phase found that mutation of rpoE significantly impacted (>2-fold) the expression of 429 total genes (205 upregulated, 224 downregulated), including multiple virulence and “housekeeping” genes. The arc operon encoding the arginine deiminase (ADI) pathway was the most upregulated in the rpoE mutant and this could be confirmed phenotypically. Taken together, these findings demonstrate that the delta (δ) subunit of RNA polymerase is vital in GAS gene expression and virulence.
Keywords: GAS; RNA-seq; Streptococcus pyogenes; arcA; rpoE; virulence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Macris M.H., Hartman N., Murray B., Klein R.F., Roberts R.B., Kaplan E.L., Horn D., Zabriskie J.B. Studies of the continuing susceptibility of group A streptococcal strains to penicillin during eight decades. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 1998;17:377–381. doi: 10.1097/00006454-199805000-00006. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

