Walnut Prevents Cognitive Impairment by Regulating the Synaptic and Mitochondrial Dysfunction via JNK Signaling and Apoptosis Pathway in High-Fat Diet-Induced C57BL/6 Mice
- PMID: 36014555
- PMCID: PMC9414791
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27165316
Walnut Prevents Cognitive Impairment by Regulating the Synaptic and Mitochondrial Dysfunction via JNK Signaling and Apoptosis Pathway in High-Fat Diet-Induced C57BL/6 Mice
Abstract
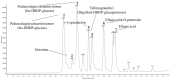
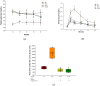
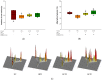
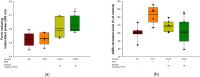
This study was conducted to evaluate the protective effect of Juglans regia (walnut, Gimcheon 1ho cultivar, GC) on high-fat diet (HFD)-induced cognitive dysfunction in C57BL/6 mice. The main physiological compounds of GC were identified as pedunculagin/casuariin isomer, strictinin, tellimagrandin I, ellagic acid-O-pentoside, and ellagic acid were identified using UPLC Q-TOF/MS analysis. To evaluate the neuro-protective effect of GC, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT), 2',7'-dichlorodihydrofluorecein diacetate (DCF-DA) analysis were conducted in H2O2 and high glucose-induced neuronal PC12 cells and hippocampal HT22 cells. GC presented significant cell viability and inhibition of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production. GC ameliorated behavioral and memory dysfunction through Y-maze, passive avoidance, and Morris water maze tests. In addition, GC reduced white adipose tissue (WAT), liver fat mass, and serum dyslipidemia. To assess the inhibitory effect of antioxidant system deficit, lipid peroxidation, ferric reducing antioxidant power (FRAP), and advanced glycation end products (AGEs) were conducted. Administration of GC protected the antioxidant damage against HFD-induced diabetic oxidative stress. To estimate the ameliorating effect of GC, acetylcholine (ACh) level, acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity, and expression of AChE and choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) were conducted, and the supplements of GC suppressed the cholinergic system impairment. Furthermore, GC restored mitochondrial dysfunction by regulating the mitochondrial ROS production and mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) levels in cerebral tissues. Finally, GC ameliorated cerebral damage by synergically regulating the protein expression of the JNK signaling and apoptosis pathway. These findings suggest that GC could provide a potential functional food source to improve diabetic cognitive deficits and neuronal impairments.
Keywords: JNK/NFκB pathway; Juglans regia; cognitive function; high-fat diet; inflammation; insulin resistance; walnut.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Neuroprotective effects of walnut (Juglans regia L.) in nervous system disorders: A comprehensive review.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024;27(12):1492-1505. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2024.79854.17302. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39539440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Green Tea Seed Oil Suppressed Aβ1⁻42-Induced Behavioral and Cognitive Deficit via the Aβ-Related Akt Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Apr 15;20(8):1865. doi: 10.3390/ijms20081865. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30991755 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-amnesic effect of Dendropanax morbifera via JNK signaling pathway on cognitive dysfunction in high-fat diet-induced diabetic mice.Behav Brain Res. 2016 Oct 1;312:39-54. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.06.013. Epub 2016 Jun 8. Behav Brain Res. 2016. PMID: 27288590
-
Ethyl Acetate Fraction from Persimmon (Diospyros kaki) Ameliorates Cerebral Neuronal Loss and Cognitive Deficit via the JNK/Akt Pathway in TMT-Induced Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 May 17;19(5):1499. doi: 10.3390/ijms19051499. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29772805 Free PMC article.
-
[The main mechanisms of development of cognitive impairment].Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2025;125(4. Vyp. 2):13-18. doi: 10.17116/jnevro202512504213. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2025. PMID: 40420446 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
The Impact of Ellagitannins and Their Metabolites through Gut Microbiome on the Gut Health and Brain Wellness within the Gut-Brain Axis.Foods. 2023 Jan 6;12(2):270. doi: 10.3390/foods12020270. Foods. 2023. PMID: 36673365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identifying Specificity Protein 2 as a key marker for diabetic encephalopathy in the context of predictive, preventive, and personalized medicine.EPMA J. 2025 Jan 10;16(1):67-93. doi: 10.1007/s13167-024-00394-0. eCollection 2025 Mar. EPMA J. 2025. PMID: 39991102
-
Mechanistic Insights into the Biological Effects and Antioxidant Activity of Walnut (Juglans regia L.) Ellagitannins: A Systematic Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Aug 10;13(8):974. doi: 10.3390/antiox13080974. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fermented Protaetia brevitarsis Larvae Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in C57BL/6 Mice via Regulation of Lipid Accumulation and Inflammation.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025 Feb 10;35:e2409025. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2409.09025. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 39947694 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effects of walnut (Juglans regia L.) in nervous system disorders: A comprehensive review.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024;27(12):1492-1505. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2024.79854.17302. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39539440 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

