Mechanistic Insights into the Pharmacological Significance of Silymarin
- PMID: 36014565
- PMCID: PMC9414257
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27165327
Mechanistic Insights into the Pharmacological Significance of Silymarin
Abstract
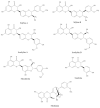
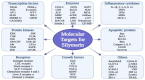
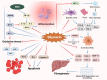
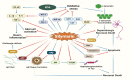
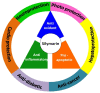
Medicinal plants are considered the reservoir of diverse therapeutic agents and have been traditionally employed worldwide to heal various ailments for several decades. Silymarin is a plant-derived mixture of polyphenolic flavonoids originating from the fruits and akenes of Silybum marianum and contains three flavonolignans, silibinins (silybins), silychristin and silydianin, along with taxifolin. Silybins are the major constituents in silymarin with almost 70-80% abundance and are accountable for most of the observed therapeutic activity. Silymarin has also been acknowledged from the ancient period and is utilized in European and Asian systems of traditional medicine for treating various liver disorders. The contemporary literature reveals that silymarin is employed significantly as a neuroprotective, hepatoprotective, cardioprotective, antioxidant, anti-cancer, anti-diabetic, anti-viral, anti-hypertensive, immunomodulator, anti-inflammatory, photoprotective and detoxification agent by targeting various cellular and molecular pathways, including MAPK, mTOR, β-catenin and Akt, different receptors and growth factors, as well as inhibiting numerous enzymes and the gene expression of several apoptotic proteins and inflammatory cytokines. Therefore, the current review aims to recapitulate and update the existing knowledge regarding the pharmacological potential of silymarin as evidenced by vast cellular, animal, and clinical studies, with a particular emphasis on its mechanisms of action.
Keywords: anti-inflammatory; antioxidant; pharmacological interventions; pro-apoptotic; silybin; silymarin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Nikam P.H., Kareparamban J., Jadhav A., Kadam V. Future Trends in Standardization of Herbal Drugs. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2012;2:38–44. doi: 10.7324/JAPS.2012.2631. - DOI
-
- Bhattacharya S. Phytotherapeutic Properties of Milk Thistle Seeds: An Overview. J. Adv. Pharm. Educ. Res. 2011;1:69–79.
-
- Das S.K., Mukherjee S., Vasudevan D.M. Medicinal Properties of Milk Thistle with Special Reference to Silymarin An Overview. Nat. Prod. Radiance. 2008;7:182–192.
-
- Ghosh A., Ghosh T., Jain S. Silymarin—A Review on the Pharmacodynamics and Bioavailability Enhancement Approaches. J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 2010;2:348–355.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

