Phytochemical Screening, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antidiabetic Activities of Different Extracts from Caralluma edulis Plant
- PMID: 36014583
- PMCID: PMC9412639
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules27165346
Phytochemical Screening, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antidiabetic Activities of Different Extracts from Caralluma edulis Plant
Abstract
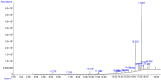
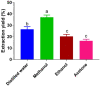
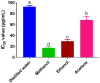
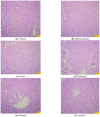
The plant Caralluma edulis is traditionally used against diabetes and inflammatory conditions in Pakistan. This study was designed to provide scientific validation of the traditional use of Caralluma edulis. Phytochemicals were extracted from the plant by different solvents (distilled water, methanol, ethanol, and acetone) using the Soxhlet's extraction method. Bioactive compounds were detected by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). The in vitro anti-inflammatory activities (albumin denaturation, membrane stabilization, and proteinase inhibition) and antioxidant capacity (DPPH scavenging activity, FRAP reducing activity) of different extracts from Caralluma edulis were assessed. The antidiabetic potential of Caralluma edulis plant extracts was determined in acute and subacute diabetic rabbit models. Oxidative stress and enzymatic antioxidant status were also estimated in MDA, CAT, and SOD levels. Results showed that the methanol extract yielded the highest contents of phenolics, flavonoids, alkaloids, and terpenoids. The in vitro anti-inflammatory activity and antioxidant potential of the methanol extract were the highest among the tested solvents. The tested extracts did not show any remarkable antidiabetic activity in the acute diabetic model. However, all tested extracts demonstrated antidiabetic potential in the subacute diabetic model. No adverse effect was observed at the tested dose (200 mg/kg) of Caralluma edulis extracts in experimental animals. It is concluded that methanol is the key solvent for extracting bioactive compounds from Caralluma edulis. The plant can be used against inflammatory disorders and may prove a potential candidate for drug development. Long-term use of Caralluma edulis at the tested dose (200 mg/kg) showed antidiabetic properties in the animal model.
Keywords: Caralluma edulis; GC-MS analysis; anti-inflammatory; antidiabetic; antioxidant; phytochemical screening; rabbits.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Malladi S., Ratnakaram V.N., Babu K.S., Sreenivasulu M. Pharmacological Review of Caralluma r.br: A Potential Herbal Genus. Asian J. Pharm. 2018;12:S1146
-
- Patel A.K., Phulwaria M., Rai M.K., Gupta A.K., Shekhawat S., Shekhawat N. In vitro propagation and ex vitro rooting of Caralluma edulis (Edgew.) Benth. & Hook. f.: An endemic and endangered edible plant species of the Thar Desert. Sci. Hortic. 2014;165:175–180. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2013.10.039. - DOI
-
- Priya D., Rajaram K., Suresh Kumar P. Phytochemical studies and GC-MS analysis of Caralluma fimbriata Wall. Int. J. Pharm. Res. Dev. 2011;3:105–110.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

