Prevalence of Protein-Energy Wasting in Dialysis Patients Using a Practical Online Tool to Compare with Other Nutritional Scores: Results of the Nutrendial Study
- PMID: 36014879
- PMCID: PMC9413877
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14163375
Prevalence of Protein-Energy Wasting in Dialysis Patients Using a Practical Online Tool to Compare with Other Nutritional Scores: Results of the Nutrendial Study
Abstract
This cross-sectional study aims to explore the prevalence of protein-energy wasting (PEW) in dialysis patients in Catalonia, Spain, using a new and practical online tool which enables rapid calculation and comparison with other nutritional scores.
Methods: A web tool (Nutrendial) was created to introduce different variables and automatically calculate PEW, Malnutrition inflammation Score (MIS) and Subjective Global Assessment (SGA) in 1389 patients (88% in haemodialysis (HD)), 12% in peritoneal dialysis (PD) from different regions of Catalonia.
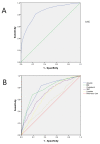
Results: A prevalence of 23.3% (26% HD, 10.2% PD) of PEW was found, with a mean MIS score of 6 and SGA score of C in 7% of the patients. ROC analysis showed MIS as the best nutritional score to diagnose PEW (AUC 0.85). Albumin delivered lower diagnostic precision (AUC 0.77) and sensitivity (66%). A cut off point of 7 (86% sensitivity and 75% specificity) for MIS and 3.7 mg/dL for albumin were found to predict the appearance of PEW in this population. SGA B or C showed an 87% sensitivity and 55% specificity to diagnose PEW. Very low nutritional intervention (14%) was recorded with this tool in patients with PEW.
Conclusions: This new online tool facilitated the calculation of PEW, enabling different professionals-including nephrologists, dieticians and nurses-to efficiently obtain insights into the nutritional status of the Catalonian dialysis population and implement the required nutritional interventions. MIS is the score with more sensitivity to diagnose PEW.
Keywords: dialysis; malnutrition inflammation score; nutritional assessment; online tool; protein-energy wasting; subjective global assessment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Carrero J.J., Stenvinkel P., Cuppari L., Ikizler T.A., Kalantar-Zadeh K., Kaysen G., Mitch W.E., Price S.R., Wanner C., Wang A.Y., et al. Etiology of the Protein-Energy Wasting Syndrome in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Consensus Statement from the International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism (ISRNM) J. Ren. Nutr. 2013;23:77–90. doi: 10.1053/j.jrn.2013.01.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fouque D., Kalantar-Zadeh K., Kopple J., Cano N., Chauveau P., Cuppari L., Franch H., Guarnieri G., Ikizler T.A., Kaysen G., et al. A proposed nomenclature and diagnostic criteria for protein-energy wasting in acute and chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2008;73:391–398. doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5002585. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

