Dietary Supplement Use among Older Cancer Survivors: Socio-Demographic Associations, Supplement Types, Reasons for Use, and Cost
- PMID: 36014907
- PMCID: PMC9414522
- DOI: 10.3390/nu14163402
Dietary Supplement Use among Older Cancer Survivors: Socio-Demographic Associations, Supplement Types, Reasons for Use, and Cost
Abstract
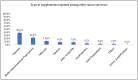
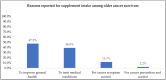
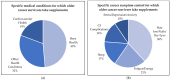
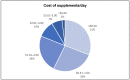
Most Americans take dietary supplements (DSs) and use is even higher among cancer survivors. This secondary analysis seeks to identify types, reasons, and costs of supplements used by 367 older cancer survivors enrolled in the Harvest for Health vegetable gardening trial and evaluate associations between supplement intake and medical/socio-demographic factors. Descriptive statistics were used to identify supplement type and reasons for use. Average market price was used to estimate cost. Fifty-nine percent of the sample reported supplement use. Female (OR 2.11, 95% CI 1.35-3.30), non-Hispanic White (OR 1.77, 95% CI 1.05-3.0), and breast and gynecological survivors (OR 1.57, 1.03-2.38) were significantly more likely to report DS use compared to males, minorities, and survivors of other cancers. Use of vitamins (39%), multivitamins (23%), and minerals (12%) were the most prevalent. Commonly reported reasons for supplement use were to improve general health (47%) or treat medical conditions (39%) and cancer-related symptoms (12%). DSs daily costs ranged from USD 0.02 to 19.81, with a mean of USD 1.28 ± 1.74, a median of USD 0.78, and a mode of USD 0.34. DS use is prevalent among older cancer survivors, with overall health reported as the leading reason for use. Out-of-pocket recurrent costs can be substantial and underscore the need to promote a nutrient-rich diet whenever possible in this vulnerable population.
Keywords: aging; cancer survivors; supplements; vitamins.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fortune Business Insights Dietary Supplements Market Size & COVID-19 Impact Analysis, By Type (Vitamins, Minerals, Enzymes, Fatty Acids, Proteins, and Others), Form (Tablets, Capsules, Liquids, and Powders, and Regional Forecasts), 2021–2022. [(accessed on 1 March 2022)]. Published January 2022. Available online: https://www.fortunebusinessinsights.com/dietary-supplements-market-102082.
-
- Mishra S., Stierman B., Gahche J.J., Potischman N. Dietary Supplement Use among Adults: United States, 2017–2018. National Center for Health Statistics; Hyattsville, MD, USA: 2021. NCHS Data Brief, no 399; - DOI
-
- United States Food & Drug Administration Dietary Supplement Products & Ingredients. [(accessed on 1 March 2022)]; Updated February 2022. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/food/dietary-supplements/dietary-supplement-products....
-
- Cowan A.E., Jun S., Gahche J.J., Tooze J.A., Dwyer J.T., Eicher-Miller H.A., Bhadra A., Guenther P.M., Potischman N., Dodd K.W., et al. Dietary Supplement Use Differs by Socioeconomic and Health-Related Characteristics among U.S. Adults, NHANES 2011–2014. Nutrients. 2018;10:1114. doi: 10.3390/nu10081114. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

