Helicobacter pylori CagA Protein Regulating the Biological Characteristics of Gastric Cancer through the miR-155-5p/SMAD2/SP1 axis
- PMID: 36014967
- PMCID: PMC9414533
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens11080846
Helicobacter pylori CagA Protein Regulating the Biological Characteristics of Gastric Cancer through the miR-155-5p/SMAD2/SP1 axis
Abstract
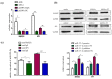
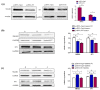
Helicobacter pylori (Hp) is a grade Ι carcinogen of gastric cancer (GC), and its high infection rate seriously affects human health. Cytotoxin-associated gene A (CagA) plays a key role in the carcinogenesis of Hp as one of its main virulence factors. miR-155-5p is abnormally expressed in patients with GC, associated with the occurrence and development of cancer. However, little is known about the association between CagA and miR-155-5p. (1) Background: This study explored the association and mechanism of CagA and miR-155-5p in GC. (2) Methods: The CagA sequence was obtained from the NCBI. After sequence optimization, it was connected to the pcDNA3.1 vector to construct a CagA eukaryotic expression plasmid (pcDNA-CagA). Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was used to investigate the expression of miR-155-5p and CagA in GC cells. The function of CagA on GC cells was detected by CCK8, wound healing, and Transwell assays. Similarly, the function of miR-155-5p was also studied through the above functional experiments after the miR-155-5p overexpression and knockdown models had successfully been constructed. The associations among CagA, miR-155-5p, and SMAD2/SP1 were evaluated using RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) and rescue experiments. (3) Results: The expression of miR-155-5p was significantly reduced in GC cells, and the expression of miR-155-5p was further reduced after CagA induction. Both overexpressed CagA and knockdown miR-155-5p cell models enhanced malignant transformation, whereas overexpressed miR-155-5p inhibited malignant transformation in vitro. The function of miR-155-5p on GC cells could be influenced by CagA. We also found that the influence of miR-155-5p on SMAD2 and SP1 could be regulated by CagA. (4) Conclusions: CagA potentially regulates the biological function of GC cells through the miR-155-5p/SMAD2/SP1 axis. miR-155-5p could be a therapeutic target for GC related to CagA.
Keywords: CagA; SMAD2; SP1; gastric cancer; miR-155-5p.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

