Molecular Targets of Pinocembrin Underlying Its Regenerative Activities in Human Keratinocytes
- PMID: 36015102
- PMCID: PMC9415973
- DOI: 10.3390/ph15080954
Molecular Targets of Pinocembrin Underlying Its Regenerative Activities in Human Keratinocytes
Abstract
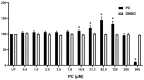
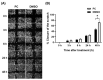
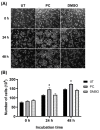
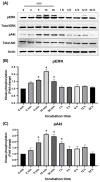
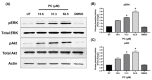
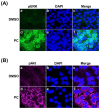
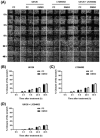
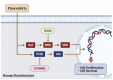
Pinocembrin is one of the well-known compounds in the group of flavonoids. The pharmacological activities of pinocembrin in association with wound-healing activities have been reported. However, its effects on the aspect of cellular interaction underlying growth and survival are still unidentified in human keratinocytes. Our previous study reported that Boesenbergia rotunda potently stimulated survival and proliferation of a human keratinocyte cell line (HaCaT). On the basis that pinocembrin is revealed to be one of the major constituents of this plant, we aimed to define the survival- and proliferation-enhancing effects of this compound at the cellular level. Results from the current study confirmed that pinocembrin induced an increase in HaCaT cell number. At the signaling perspective, we identified that pinocembrin significantly triggered ERK1/2 and Akt activation. The stimulating effects of pinocembrin were clearly inhibited by MEK and PI3K inhibitors authenticating that proliferation- and survival-promoting activities of pinocembrin were mainly acted on these two signaling cascades. Altogether, we successfully identified that pinocembrin functions to induce keratinocyte proliferation and survival, at least by provoking MAPK and PI3K pathways. Our study encourages the fact that pinocembrin is one of the interesting natural flavonoid compounds to be developed as a wound closure-promoting agent.
Keywords: flavonoids; keratinocyte; pinocembrin; regenerative medicine; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

