Immunomodulatory Effects of (R)-Sulforaphane on LPS-Activated Murine Immune Cells: Molecular Signaling Pathways and Epigenetic Changes in Histone Markers
- PMID: 36015113
- PMCID: PMC9414446
- DOI: 10.3390/ph15080966
Immunomodulatory Effects of (R)-Sulforaphane on LPS-Activated Murine Immune Cells: Molecular Signaling Pathways and Epigenetic Changes in Histone Markers
Abstract
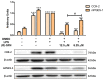
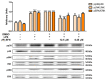
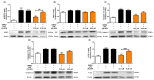
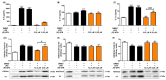
The aim of this study was to explore the immunomodulatory effects of the natural enantiomer (R)-Sulforaphane (SFN) and the possible signaling pathways involved in an ex vivo model of LPS-stimulated murine peritoneal macrophages. Furthermore, we studied the epigenetic changes induced by (R)-SFN as well as the post-translational modifications of histone H3 (H3K9me3 and H3K18ac) in relation to the production of cytokines in murine splenocytes after LPS stimulation. (R)-SFN was able to modulate the inflammatory response and oxidative stress induced by LPS stimulation in murine peritoneal macrophages through the inhibition of reactive oxygen species (ROS), nitric oxide (NO) and cytokine (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-17, IL-18 and TNF-α) production by down-regulating the expression of pro-inflammatory enzymes (iNOS, COX-2 and mPGES-1). We also found that activation of the Nrf-2/HO-1 axis and inhibition of the JAK2/STAT-3, MAPK, canonical and non-canonical inflammasome signaling pathways could have been responsible for the immunomodulatory effects of (R)-SFN. Furthermore, (R)-SFN modulated epigenetic modifications through histone methylation (H3K9me3) and deacetylation (H3K18ac) in LPS-activated spleen cells. Collectively, our results suggest that (R)-SFN could be a promising epinutraceutical compound for the management of immunoinflammatory diseases.
Keywords: (R)-sulforaphane; antioxidant; epigenetic; histone; inflammation; macrophages; spleen cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Effects of Oleacein, a New Epinutraceutical Bioproduct from Extra Virgin Olive Oil, in LPS-Activated Murine Immune Cells.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Oct 28;15(11):1338. doi: 10.3390/ph15111338. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36355509 Free PMC article.
-
(R)-8-Methylsulfinyloctyl isothiocyanate from Nasturtium officinale inhibits LPS-induced immunoinflammatory responses in mouse peritoneal macrophages: chemical synthesis and molecular signaling pathways involved.Food Funct. 2023 Jul 31;14(15):7270-7283. doi: 10.1039/d3fo02009f. Food Funct. 2023. PMID: 37469300
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Sulforaphane on LPS-Activated Microglia Potentially through JNK/AP-1/NF-κB Inhibition and Nrf2/HO-1 Activation.Cells. 2019 Feb 22;8(2):194. doi: 10.3390/cells8020194. Cells. 2019. PMID: 30813369 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of mitochondrial functions by the indirect antioxidant sulforaphane: a seemingly contradictory dual role and an integrative hypothesis.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Dec;65:1078-1089. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.08.182. Epub 2013 Aug 30. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23999506 Review.
-
Anticancer Activity of Sulforaphane: The Epigenetic Mechanisms and the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018 Jun 6;2018:5438179. doi: 10.1155/2018/5438179. eCollection 2018. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018. PMID: 29977456 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Multifaceted Health Benefits of Broccoli-A Review of Glucosinolates, Phenolics and Antimicrobial Peptides.Molecules. 2025 May 22;30(11):2262. doi: 10.3390/molecules30112262. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40509149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunomodulatory Effects and Regulatory Mechanisms of (R)-6-HITC, an Isothiocyanate from Wasabi (Eutrema japonicum), in an Ex Vivo Mouse Model of LPS-Induced Inflammation.J Agric Food Chem. 2024 Oct 2;72(39):21520-21532. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.4c02943. Epub 2024 Sep 19. J Agric Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 39298284 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of immune cum inflammatory pathway by earthworm granulation tissue extract in wound healing of diabetic rabbit model.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 27;10(3):e24909. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24909. eCollection 2024 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2024. Retraction in: Heliyon. 2025 Mar 18;11(8):e43209. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2025.e43209. PMID: 38333811 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
-
- Vergara F., Wenzler M., Hansen B.G., Kliebenstein D.J., Halkier B.A., Gershenzon J., Schneider B. Determination of the absolute configuration of the glucosinolate methyl sulfoxide group reveals a stereospecific biosynthesis of the side chain. Phytochemistry. 2008;69:2737–2742. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2008.09.008. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

