The Current State of the Art in PARP Inhibitor-Based Delivery Nanosystems
- PMID: 36015275
- PMCID: PMC9413625
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14081647
The Current State of the Art in PARP Inhibitor-Based Delivery Nanosystems
Abstract
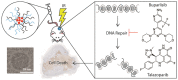
Poly (adenosine diphosphate [ADP]-ribose) polymerases inhibitors (PARPi), the first clinically approved drug that exhibits synthetic lethality, are moving to the forefront of cancer treatments. Currently, the oral bioavailability of PARPi is quite low; thus, it is a major challenge to effectively and safely deliver PARPi during clinical cancer therapy. Nanotechnology has greatly advanced the development of drug delivery. Based on the basic characteristics and various forms of nanoparticles, drug delivery systems can prolong the time that drugs circulate, realize the controlled release of drugs, provide drugs with an active targeting ability, and spatiotemporally present combination treatment. Furthermore, nanosystems may not only enhance drug efficiency but also reduce adverse side effects. This review focuses on strategies involving nanoparticle-based delivery for PARPi, including single administration and codelivery with other agents. We believe that nanosystems have great potential in advancing PARPi efficacy for cancer therapy.
Keywords: PARP inhibitor; cancer therapy; drug delivery; nanosystem.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase-1 Inhibitors Drug Discovery, Design, and Development as Anticancer Agents from Past to Present: A Mini-Review.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2022;22(12):1597-1606. doi: 10.2174/1389557521666210929144045. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 34587882 Review.
-
The role of novel poly (ADP-ribose) inhibitors in the treatment of locally advanced and metastatic Her-2/neu negative breast cancer with inherited germline BRCA1/2 mutations. A review of the literature.J Med Life. 2021 Jan-Mar;14(1):17-20. doi: 10.25122/jml-2020-0132. J Med Life. 2021. PMID: 33767780 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PARP inhibitor resistance: the underlying mechanisms and clinical implications.Mol Cancer. 2020 Jun 20;19(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01227-0. Mol Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32563252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor therapeutic effect: are we just scratching the surface?Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2015;19(9):1149-52. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2015.1073262. Epub 2015 Jul 27. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2015. PMID: 26212149
-
Therapeutic Targeting of Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase-1 (PARP1) in Cancer: Current Developments, Therapeutic Strategies, and Future Opportunities.Med Res Rev. 2017 Nov;37(6):1461-1491. doi: 10.1002/med.21442. Epub 2017 May 16. Med Res Rev. 2017. PMID: 28510338 Review.
Cited by
-
Co-Packaged PARP inhibitor and photosensitizer for targeted photo-chemotherapy of 3D ovarian cancer spheroids.Cell Biosci. 2024 Feb 6;14(1):20. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01197-6. Cell Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38321470 Free PMC article.
-
Expanding the Perspective on PARP1 and Its Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy: From DNA Damage Repair to Immunomodulation.Biomedicines. 2024 Jul 20;12(7):1617. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071617. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39062190 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Different Commercial Sealing Hemostatic Patches for Their Selection as Reservoirs for Localized Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2025 Jan 8;8(2):499-509. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.4c00608. eCollection 2025 Feb 14. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2025. PMID: 39974645
-
Role of PARP Inhibitors in Cancer Immunotherapy: Potential Friends to Immune Activating Molecules and Foes to Immune Checkpoints.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 16;14(22):5633. doi: 10.3390/cancers14225633. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428727 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted Nanocarrier-Based Drug Delivery Strategies for Improving the Therapeutic Efficacy of PARP Inhibitors against Ovarian Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 30;25(15):8304. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158304. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125873 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
- 82001932/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81972693/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 2022R005/The university level scientific research project of Zhejiang Shuren University
- non/Training plan for leading talents from Universities in Zhejiang Province
- LR20H160001/Zhejiang Provincial Nature Science Foundation of China
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

