The Potential of Topoisomerase Inhibitor-Based Antibody-Drug Conjugates
- PMID: 36015333
- PMCID: PMC9413092
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14081707
The Potential of Topoisomerase Inhibitor-Based Antibody-Drug Conjugates
Abstract
DNA topoisomerases are essential enzymes that stabilize DNA supercoiling and resolve entanglements. Topoisomerase inhibitors have been widely used as anti-cancer drugs for the past 20 years. Due to their selectivity as topoisomerase I (TOP1) inhibitors that trap TOP1 cleavage complexes, camptothecin and its derivatives are promising anti-cancer drugs. To increase accumulation of TOP1 inhibitors in cancer cells through the targeting of tumors, TOP1 inhibitor antibody-drug conjugates (TOP1-ADC) have been developed and marketed. Some TOP1-ADCs have shown enhanced therapeutic efficacy compared to prototypical anti-cancer ADCs, such as T-DM1. Here, we review various types of camptothecin-based TOP1 inhibitors and recent developments in TOP1-ADCs. We then propose key points for the design and construction of TOP1-ADCs. Finally, we discuss promising combinatorial strategies, including newly developed approaches to maximizing the therapeutic potential of TOP1-ADCs.
Keywords: anti-cancer drug; antibody–drug conjugates; targeted drug delivery; topoisomerase 1; topoisomerase inhibitor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



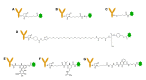
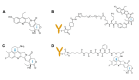
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

