Diagnostic Tools for Rapid Screening and Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Infection
- PMID: 36016088
- PMCID: PMC9414050
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines10081200
Diagnostic Tools for Rapid Screening and Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Abstract
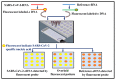
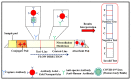
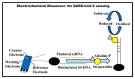
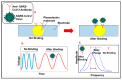
The novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), has severely impacted human health and the health management system globally. The ongoing pandemic has required the development of more effective diagnostic strategies for restricting deadly disease. For appropriate disease management, accurate and rapid screening and isolation of the affected population is an efficient means of containment and the decimation of the disease. Therefore, considerable efforts are being directed toward the development of rapid and robust diagnostic techniques for respiratory infections, including SARS-CoV-2. In this article, we have summarized the origin, transmission, and various diagnostic techniques utilized for the detection of the SARS-CoV-2 virus. These higher-end techniques can also detect the virus copy number in asymptomatic samples. Furthermore, emerging rapid, cost-effective, and point-of-care diagnostic devices capable of large-scale population screening for COVID-19 are discussed. Finally, some breakthrough developments based on spectroscopic diagnosis that could revolutionize the field of rapid diagnosis are discussed.
Keywords: COVID-19/SARS-CoV-2; aptamers; biosensors; immunodiagnostics techniques; nucleic acid hybridization; surface plasmon resonance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Modelling of hypothetical SARS-CoV-2 point-of-care tests on admission to hospital from A&E: rapid cost-effectiveness analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2021 Mar;25(21):1-68. doi: 10.3310/hta25210. Health Technol Assess. 2021. PMID: 33764295 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid COVID-19 Molecular Diagnostic System Using Virus Enrichment Platform.Biosensors (Basel). 2021 Oct 6;11(10):373. doi: 10.3390/bios11100373. Biosensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34677329 Free PMC article.
-
How Nanophotonic Label-Free Biosensors Can Contribute to Rapid and Massive Diagnostics of Respiratory Virus Infections: COVID-19 Case.ACS Sens. 2020 Sep 25;5(9):2663-2678. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.0c01180. Epub 2020 Aug 24. ACS Sens. 2020. PMID: 32786383 Review.
-
Universal screening for SARS-CoV-2 infection: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Sep 15;9(9):CD013718. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013718. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33502003 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic and pregnancy.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Jun;222(6):521-531. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.03.021. Epub 2020 Mar 23. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2020. PMID: 32217113 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Electrochemical Sensors in Enhancing HIV Detection.Curr HIV Res. 2025;23(1):2-13. doi: 10.2174/011570162X363311250206045837. Curr HIV Res. 2025. PMID: 39950463 Review.
-
Lateral Flow Immunoassays for SARS-CoV-2.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Nov 18;12(11):2854. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12112854. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36428918 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Associated Biochemical and Hematological Markers in COVID-19 Severity Prediction.Adv Med. 2023 Oct 19;2023:6216528. doi: 10.1155/2023/6216528. eCollection 2023. Adv Med. 2023. PMID: 37900669 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of potential biomarkers and drug of ischemic stroke in patients with COVID-19 through machine learning.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 11;10(20):e39039. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39039. eCollection 2024 Oct 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39502238 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting Severe Respiratory Failure in Patients with COVID-19: A Machine Learning Approach.J Clin Med. 2024 Dec 4;13(23):7386. doi: 10.3390/jcm13237386. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39685844 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

