Evolutionary Conservation of PP2A Antagonism and G2/M Cell Cycle Arrest in Maedi-Visna Virus Vif
- PMID: 36016323
- PMCID: PMC9413702
- DOI: 10.3390/v14081701
Evolutionary Conservation of PP2A Antagonism and G2/M Cell Cycle Arrest in Maedi-Visna Virus Vif
Abstract
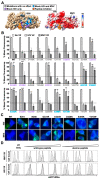
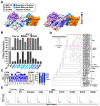
The canonical function of lentiviral Vif proteins is to counteract the mutagenic potential of APOBEC3 antiviral restriction factors. However, recent studies have discovered that Vif proteins from diverse HIV-1 and simian immunodeficiency virus (SIV) isolates degrade cellular B56 phosphoregulators to remodel the host phosphoproteome and induce G2/M cell cycle arrest. Here, we evaluate the conservation of this activity among non-primate lentiviral Vif proteins using fluorescence-based degradation assays and demonstrate that maedi-visna virus (MVV) Vif efficiently degrades all five B56 family members. Testing an extensive panel of single amino acid substitution mutants revealed that MVV Vif recognizes B56 proteins through a conserved network of electrostatic interactions. Furthermore, experiments using genetic and pharmacologic approaches demonstrate that degradation of B56 proteins requires the cellular cofactor cyclophilin A. Lastly, MVV Vif-mediated depletion of B56 proteins induces a potent G2/M cell cycle arrest phenotype. Therefore, remodeling of the cellular phosphoproteome and induction of G2/M cell cycle arrest are ancient and conserved functions of lentiviral Vif proteins, which suggests that they are advantageous for lentiviral pathogenesis.
Keywords: HIV-1; MVV; PPP2R5; Vif; host-pathogen; phosphatase regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

