Identification of PARP12 Inhibitors By Virtual Screening and Molecular Dynamics Simulations
- PMID: 36016564
- PMCID: PMC9395932
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.847499
Identification of PARP12 Inhibitors By Virtual Screening and Molecular Dynamics Simulations
Abstract
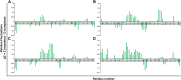
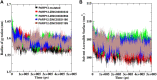
Poly [adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-ribose] polymerases (PARPs) are members of a family of 17 enzymes that performs several fundamental cellular processes. Aberrant activity (mutation) in PARP12 has been linked to various diseases including inflammation, cardiovascular disease, and cancer. Herein, a large library of compounds (ZINC-FDA database) has been screened virtually to identify potential PARP12 inhibitor(s). The best compounds were selected on the basis of binding affinity scores and poses. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulation and binding free energy calculation (MMGBSA) were carried out to delineate the stability and dynamics of the resulting complexes. To this end, root means deviations, relative fluctuation, atomic gyration, compactness, covariance, residue-residue contact map, and free energy landscapes were studied. These studies have revealed that compounds ZINC03830332, ZINC03830554, and ZINC03831186 are promising agents against mutated PARP12.
Keywords: MD simulations; MMGBSA; PARP12; ZINC-FDA; virtual screening.
Copyright © 2022 Almeleebia, Ahamad, Ahmad, Alshehri, Alkhathami, Alshahrani, Asiri, Saeed, Siddiqui, Yadav and Saeed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Unveiling Promising PARP12 Inhibitors through Virtual Screening for Cancer Therapy.Curr Pharm Des. 2025 Apr 22. doi: 10.2174/0113816128369323250322044605. Online ahead of print. Curr Pharm Des. 2025. PMID: 40265429
-
Screening and design of PARP12 inhibitors from traditional Chinese medicine small molecules using computational modeling and simulation.J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024 Nov 11:1-14. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2024.2424941. Online ahead of print. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2024. PMID: 39527026
-
PARP1-produced poly-ADP-ribose causes the PARP12 translocation to stress granules and impairment of Golgi complex functions.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 25;7(1):14035. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-14156-8. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29070863 Free PMC article.
-
The diverse biological roles of mammalian PARPS, a small but powerful family of poly-ADP-ribose polymerases.Front Biosci. 2008 Jan 1;13:3046-82. doi: 10.2741/2909. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 17981777 Review.
-
ADP-ribosylation and intracellular traffic: an emerging role for PARP enzymes.Biochem Soc Trans. 2019 Feb 28;47(1):357-370. doi: 10.1042/BST20180416. Epub 2019 Feb 1. Biochem Soc Trans. 2019. PMID: 30710058 Review.
Cited by
-
Fc-Binding Cyclopeptide Induces Allostery from Fc to Fab: Revealed Through in Silico Structural Analysis to Anti-Phenobarbital Antibody.Foods. 2025 Apr 15;14(8):1360. doi: 10.3390/foods14081360. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40282765 Free PMC article.
-
The Regulatory Network of Gastric Cancer Pathogenesis and Its Potential Therapeutic Active Ingredients of Traditional Chinese Medicine Based on Bioinformatics, Molecular Docking, and Molecular Dynamics Simulation.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Nov 26;2022:5005498. doi: 10.1155/2022/5005498. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 36471693 Free PMC article.
-
Unravelling driver genes as potential therapeutic targets in ovarian cancer via integrated bioinformatics approach.J Ovarian Res. 2024 Apr 23;17(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s13048-024-01402-7. J Ovarian Res. 2024. PMID: 38654363 Free PMC article.
-
In silico study to identify novel NEK7 inhibitors from natural sources by a combination strategy.Mol Divers. 2025 Feb;29(1):139-162. doi: 10.1007/s11030-024-10838-4. Epub 2024 Apr 10. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 38598164
-
Synthesizing network pharmacology, bioinformatics, and in vitro experimental verification to screen candidate targets of Salidroside for mitigating Alzheimer's disease.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Apr;398(4):4539-4558. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03555-0. Epub 2024 Nov 6. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39503755
References
-
- Abraham M. J., Murtola T., Schulz R., Páll S., Smith J. C., Hess B., et al. (2015). GROMACS: High Performance Molecular Simulations through Multi-Level Parallelism from Laptops to Supercomputers. SoftwareX 1-2, 19–25. 10.1016/j.softx.2015.06.001 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

