Identification of PARP12 Inhibitors By Virtual Screening and Molecular Dynamics Simulations
- PMID: 36016564
- PMCID: PMC9395932
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.847499
Identification of PARP12 Inhibitors By Virtual Screening and Molecular Dynamics Simulations
Abstract
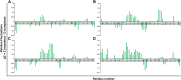
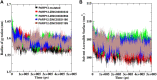
Poly [adenosine diphosphate (ADP)-ribose] polymerases (PARPs) are members of a family of 17 enzymes that performs several fundamental cellular processes. Aberrant activity (mutation) in PARP12 has been linked to various diseases including inflammation, cardiovascular disease, and cancer. Herein, a large library of compounds (ZINC-FDA database) has been screened virtually to identify potential PARP12 inhibitor(s). The best compounds were selected on the basis of binding affinity scores and poses. Molecular dynamics (MD) simulation and binding free energy calculation (MMGBSA) were carried out to delineate the stability and dynamics of the resulting complexes. To this end, root means deviations, relative fluctuation, atomic gyration, compactness, covariance, residue-residue contact map, and free energy landscapes were studied. These studies have revealed that compounds ZINC03830332, ZINC03830554, and ZINC03831186 are promising agents against mutated PARP12.
Keywords: MD simulations; MMGBSA; PARP12; ZINC-FDA; virtual screening.
Copyright © 2022 Almeleebia, Ahamad, Ahmad, Alshehri, Alkhathami, Alshahrani, Asiri, Saeed, Siddiqui, Yadav and Saeed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Abraham M. J., Murtola T., Schulz R., Páll S., Smith J. C., Hess B., et al. (2015). GROMACS: High Performance Molecular Simulations through Multi-Level Parallelism from Laptops to Supercomputers. SoftwareX 1-2, 19–25. 10.1016/j.softx.2015.06.001 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

