Mechanism Study of Cinnamomi Ramulus and Paris polyphylla Sm. Drug Pair in the Treatment of Adenomyosis by Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation
- PMID: 36016675
- PMCID: PMC9398691
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2624434
Mechanism Study of Cinnamomi Ramulus and Paris polyphylla Sm. Drug Pair in the Treatment of Adenomyosis by Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation
Abstract
Objective: To explore the molecular mechanism of the Cinnamomi ramulus and Paris polyphylla Sm. (C-P) drug pair in the treatment of adenomyosis (AM) based on network pharmacology and animal experiments.
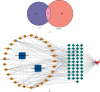
Methods: Via a network pharmacology strategy, a drug-component-target-disease network (D-C-T-D) and protein-protein interaction (PPI) network were constructed to explore the core components and key targets of C-P drug pair therapy for AM, and the core components and key targets were verified by molecular docking. Based on the results of network pharmacology, animal experiments were performed for further verification. The therapeutic effect of the C-P drug pair on uterine ectopic lesions was evaluated in a constructed AM rat model.
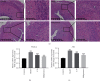
Results: A total of 30 components and 45 corresponding targets of C-P in the treatment of AM were obtained through network pharmacology. In the D-C-T-D network and PPI network, 5 core components and 10 key targets were identified. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis showed that the PI3K signaling pathway was the most significantly enriched nontumor pathway. Molecular docking showed that most of the core components and key targets docked completely. Animal experiments showed that the C-P drug pair significantly ameliorated the pathological changes of endometriotic lesions in AM model rats and inhibited PI3K and Akt gene expression, and PI3K and Akt protein phosphorylation. In addition, treatment with the C-P drug pair promoted AM cell apoptosis; upregulated the protein expression of Bax, Caspase-3, and cleaved Caspase-9; and restrained Bcl-2 expression.
Conclusions: We propose that the pharmacological mechanism of the C-P drug pair in the treatment of AM is related to inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway and promotion of apoptosis in AM ectopic lesions.
Copyright © 2022 Keke Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no financial or scientific conflicts of interest with regard to the research described in this manuscript.
Figures




Similar articles
-
[Study on mechanism of Rhei Radix et Rhizoma-Persicae Semen in treatment of adenomyosis based on network pharmacology].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020 Sep;45(17):4112-4119. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200520.403. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33164395 Chinese.
-
Network pharmacology combined with molecular docking and experimental validation to explore the potential mechanism of Cinnamomi ramulus against ankylosing spondylitis.Ann Med. 2023;55(2):2287193. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2023.2287193. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Ann Med. 2023. PMID: 38019769 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification to Explore the Pharmacological Mechanisms of Aloin Against Gastric Cancer.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022 Jun 20;16:1947-1961. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S360790. eCollection 2022. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2022. PMID: 35757520 Free PMC article.
-
Erianin, the main active ingredient of Dendrobium chrysotoxum Lindl, inhibits precancerous lesions of gastric cancer (PLGC) through suppression of the HRAS-PI3K-AKT signaling pathway as revealed by network pharmacology and in vitro experimental verification.J Ethnopharmacol. 2021 Oct 28;279:114399. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114399. Epub 2021 Jul 8. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34246740
-
[Mechanism of Bupleurum scorzonerifolium and Paeonia lactiflora herbal pair against liver cancer: an exploration based on UPLC-Q-TOF-MS combined with network pharmacology].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 Jul;47(13):3597-3608. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220110.402. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35850814 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Integrated multi-omics analysis and experimental verification reveal the involvement of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in myometrial fibrosis of adenomyosis.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 20;15(1):13637. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-98369-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40254638 Free PMC article.
-
Research Advances in Adenomyosis-Related Signaling Pathways and Promising Targets.Biomolecules. 2024 Nov 4;14(11):1402. doi: 10.3390/biom14111402. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39595579 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abbott J. A. Adenomyosis and abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB-A)-pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. Best Practice & Research Clinical Obstetrics & Gynaecology . 2017;40:68–81. - PubMed
-
- Pontis A., D’Alterio M. N., Pirarba S., de Angelis C., Tinelli R., Angioni S. Adenomyosis: a systematic review of medical treatment. Gynecological Endocrinology . 2016;32(9):696–700. - PubMed
-
- Huang J. M., Hu G. H., Wan Y. T., et al. Clinical effect of yushen huoxue formula on adenomyosis secondary pain and blood stasis syndrome. Journal of Beijing University of Traditional Chinese Medicine . 2022;45(1):73–80.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

