Tibetan Medicine Shi-Wei-Gan-Ning-San Alleviates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Chronic Liver Injury by Inhibiting TGF- β 1 in Wistar Rats
- PMID: 36016677
- PMCID: PMC9398689
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2011876
Tibetan Medicine Shi-Wei-Gan-Ning-San Alleviates Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Chronic Liver Injury by Inhibiting TGF- β 1 in Wistar Rats
Abstract
Background: Shi-Wei-Gan-Ning-San (SWGNS) is a classic Tibetan prescription, which has obvious clinical effects in the treatment of viral hepatitis, fatty liver, liver fibrosis, liver cirrhosis, liver cancer, and other liver injuries. However, animal studies and mechanism studies are still lacking. This study aimed to investigate its hepatoprotective efficacy and pharmacological mechanism in animal experiments.
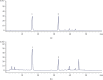
Methods: Chronic liver injury was induced by oral administration of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) in Wistar rats for 13 weeks. SWGNS was administered orally to rats at doses of 235, 705, and 1410 mg/kg for 13 weeks. Blood samples were collected for biochemical, ELISA, and radioimmunoassay. Livers were harvested for H&E and immunohistochemical staining. The major constituents of SWGNS were analyzed by HPLC. In vitro experiments were used to explore the protective effect of Crocin on BRL-3A in the environment of H2O2.
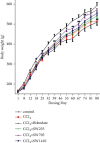
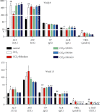
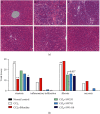
Results: SWGNS reversed weight loss is induced by CCl4. Serum assays showed that SWGNS reduced CCl4-induced alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, total bilirubin, and γ-glutamyltransferase levels and increased the total protein and albumin levels. Histopathological evaluation showed that SWGNS alleviated hepatic steatosis, fibrosis, and inflammation. Furthermore, SWNGS reduced CCl4-induced elevations of TGF-β1, hyaluronic acid, laminin, and collagen IV in serum and reduced the high expression of α-SMA in tissues. Moreover, Crocin I and II are the main components of SWGNS. Crocin attenuated the damaging effects of H2O2 on BRL-3A.
Conclusions: In conclusion, SWGNS alleviated CCl4-induced chronic liver injury by inhibiting the TGF-β1 pathway. This plays an important role in promoting traditional Tibetan medicine in clinical practice.
Copyright © 2022 Ziming Jia et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hepatoprotective effect of total flavonoids of Mallotus apelta (Lour.) Muell.Arg. leaf against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in rats via modulation of TGF-β1/Smad and NF-κB signaling pathways.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 May 23;254:112714. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112714. Epub 2020 Feb 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32105750
-
Protective effects of Foeniculum vulgare root bark extract against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrosis in mice.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Aug 21;23(31):5722-5731. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i31.5722. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28883697 Free PMC article.
-
Tibetan Medical Formula Shi-Wei-Gan-Ning-Pill Protects Against Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Liver Fibrosis - An NMR-Based Metabolic Profiling.Front Pharmacol. 2018 Aug 29;9:965. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00965. eCollection 2018. Front Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30210344 Free PMC article.
-
[Protective effect and mechanism of total lignans from Tibetan medicinal Herpetospermum seeds on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in rats].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017 Feb;42(3):567-571. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20161222.063. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28952266 Chinese.
-
Extract of Averrhoacarambola L. (Oxalidaceae) roots ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Jan;121:109516. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109516. Epub 2019 Nov 5. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 31704616
Cited by
-
Antioxidant and Antiapoptotic Properties of n-Butanol Fraction the Acanthopanax senticosus Extracts in H2O2-RAW264.7 Cells and CCl4-Induced Liver Injury in Mice.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023 Feb 23;2023:9190198. doi: 10.1155/2023/9190198. eCollection 2023. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2023. PMID: 36874619 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ain Q. T. Hepatotoxicity induced by intravenous administration of PEGylated nano-graphene oxide in albino mice. Materials Express . 2021;11
-
- Choi D. J., Kim S. C., Park G. E., et al. Protective effect of a mixture of Astragalus membranaceus and lithospermum erythrorhizon extract against hepatic steatosis in high fat diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease mice. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine . 2020;2020:11. doi: 10.1155/2020/8370698.8370698 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

