Effects of caffeine, methylliberine, and theacrine on vigilance, marksmanship, and hemodynamic responses in tactical personnel: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial
- PMID: 36016763
- PMCID: PMC9397462
- DOI: 10.1080/15502783.2022.2113339
Effects of caffeine, methylliberine, and theacrine on vigilance, marksmanship, and hemodynamic responses in tactical personnel: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Tactical athletes require fast reaction times (RT) along with high levels of vigilance and marksmanship performance. Caffeine has been shown to improve these measures but also results in increased blood pressure and jitteriness. Research on other purine alkaloids, such as methylliberine and theacrine, has suggested they do not increase blood pressure or jitteriness to the same extent, but their impact on tactical performance is unknown.
Methods: A between-subjects, randomized, placebo-controlled design was used to test the effects of placebo (PLA), 300 mg caffeine (CAF), and a combination of 150 mg caffeine, 100 mg methylliberine, and 50 mg theacrine (CMT) on RT and marksmanship along with hemodynamic and arousal measures following a sustained vigilance task in tactical personnel (n = 48). Following consumption of the supplement, participants underwent a 150-min protocol consisting of two rounds. Each round began with leisurely reading followed by a 30-min vigilance task before beginning two trials of movement and marksmanship tasks. Hemodynamics and felt arousal were assessed throughout the protocol. Composite Z-scores were calculated for overall performance measures at each timepoint, and mixed-effects models were used to assess differences in RT, accuracy, and composite Z-scores along with hemodynamics and felt arousal. An α-level of 0.05 was used to determine statistical significance, and Cohen's d was used to quantify effect sizes.
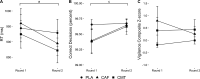
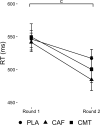
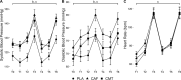
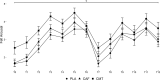
Results: A Group-by-Time interaction for vigilance RT (P = 0.038) indicated improvements for both CAF and CMT from round 1 to round 2 (P < 0.01) while PLA did not change (P = 0.27). No Group main effects or Group-by-Time interactions were found for movement or marksmanship performance (P > 0.20). Group main effects for systolic (SBP; P = 0.001) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP; P = 0.028) indicated higher SBP in CAF (P = 0.003, d= 0.84) and CMT (P = 0.007, d= 0.79) compared to PLA but only higher DBP in CAF (P = 0.025, d= 0.74). No Group-by-Time interaction or Group main effect was found for felt arousal (P > 0.16).
Conclusions: These findings suggest similar benefits on RT during a vigilance task between CAF, containing 300 mg caffeine, and CMT above PLA, though CAF resulted in slightly less favorable hemodynamic changes. This study is the first to provide data showing similar efficacy of combined caffeine, methylliberine, and theacrine compared to double the caffeine dose consumed alone on vigilance RT but without a significant rise in DBP above PLA in tactical personnel.
Keywords: Sports nutrition; dietary supplements; reaction time; stimulants.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effect of single or combined caffeine and L-Theanine supplementation on shooting and cognitive performance in elite curling athletes: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2023 Dec;20(1):2267536. doi: 10.1080/15502783.2023.2267536. Epub 2023 Oct 10. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2023. PMID: 37815006 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Development of a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) method for characterizing caffeine, methylliberine, and theacrine pharmacokinetics in humans.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2020 Oct 15;1155:122278. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2020.122278. Epub 2020 Aug 2. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32829142
-
Caffeine ingestion changes time-motion and technical-tactical aspects in simulated boxing matches: A randomized double-blind PLA-controlled crossover study.Eur J Sport Sci. 2018 Aug;18(7):975-983. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2018.1465599. Epub 2018 May 8. Eur J Sport Sci. 2018. PMID: 29738282 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of Caffeine and Nitrates Combination on Exercise Performance, Heart Rate and Oxygen Uptake: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 2;16(19):3352. doi: 10.3390/nu16193352. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39408319 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of creatine and caffeine ingestion in combination on exercise performance: A systematic review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023;63(20):4785-4798. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2021.2007470. Epub 2021 Nov 30. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 34845944
Cited by
-
Methylliberine Ingestion Improves Various Indices of Affect but Not Cognitive Function in Healthy Men and Women.Nutrients. 2023 Oct 24;15(21):4509. doi: 10.3390/nu15214509. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37960163 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dose response effects of theacrine on cognitive performance and subsequent sleep.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 19;14(1):28614. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79046-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39562624 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic insights into the Arabica-like flavour of stenophylla coffee and the chemistry of quality coffee.NPJ Sci Food. 2025 Mar 19;9(1):33. doi: 10.1038/s41538-025-00398-8. NPJ Sci Food. 2025. PMID: 40108189 Free PMC article.
-
A caffeine and theacrine combination improves cognitive performance in tactical personnel under physically fatiguing conditions.J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2025 Dec;22(1):2536146. doi: 10.1080/15502783.2025.2536146. Epub 2025 Jul 22. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40693646 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Scofield DE, Kardouni JR.. The tactical athlete. Strength Conditioning J. 2015;37(4):2–7.
-
- Austin KG, Deuster P. Monitoring training for human performance optimization. J Spec Oper Med. 2015;15(2):102–108. . - PubMed
-
- Faudone G, Arifi S, Merk D. The medicinal chemistry of caffeine. J Med Chem. 2021. Jun;64(11):7156–7178. - PubMed
-
- Horst K, Jenkins WL. The effect of caffeine, coffee and decaffeinated coffee upon blood pressure, pulse rate and simple reaction time of men of various ages. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1935. Apr;53(4):385–400.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
