Assisted dispersal and reproductive success in an ant species with matchmaking
- PMID: 36016821
- PMCID: PMC9398888
- DOI: 10.1002/ece3.9236
Assisted dispersal and reproductive success in an ant species with matchmaking
Abstract
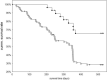
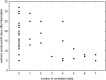
Workers of the ant Cardiocondyla elegans drop female sexuals into the nest entrance of other colonies to promote outbreeding with unrelated, wingless males. Corroborating the results from previous years, we document that carrier and carried female sexuals are typically related and that the transfer initially occurs mostly from their joint natal colonies to unrelated colonies. Female sexuals mate multiply with up to seven genetically distinguishable males. Contrary to our expectation, the colony growth rate of multiple-mated and outbred female sexuals was lower than that of inbred or single-mated females, leading to the question of why female sexuals mate multiply at all. Despite the obvious costs, multiple mating might be a way for female sexuals to "pay rent" for hibernation in an alien nest. We argue that in addition to evade inbreeding depression from regular sibling mating over many generations, assisted dispersal might also be a strategy for minimizing the risk of losing all reproductive investment when nests are flooded in winter.
Keywords: Formicidae; Hymenoptera; mating behavior; outbreeding; polyandry; population structure.
© 2022 The Authors. Ecology and Evolution published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Bonte, D. , Van Belle, S. , & Maelfait, J.‐P. (2007). Maternal care and reproductive state‐dependent mobility determine natal dispersal in a wolf spider. Animal Behaviour, 74, 63–69. 10.1016/j.anbehav.2006.06.021 - DOI
-
- Fernández‐Escudero, I. , Seppä, P. , & Pamilo, P. L. (2001). Dependent colony founding in the ant Proformica longiseta . Insectes Sociaux, 48, 80–82. 10.1007/PL00001750 - DOI
-
- Frasier, T. (2018). Related package, version 1.0, for R software‐4.0.3.
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

