Characteristics and trends of the most cited papers in robotic assisted arthroplasty
- PMID: 36016864
- PMCID: PMC9395732
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jor.2022.07.025
Characteristics and trends of the most cited papers in robotic assisted arthroplasty
Abstract
Purpose: To compile and analyze the top 50 most frequently cited articles published on robotic-assisted arthroplasty, allowing clinicians to effectively identify the most influential literature pertaining to this topic.
Methods: Guidelines set by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews were used as the foundation for data collection and analysis. All papers pertaining to robotic-assisted arthroplasty were retrieved using the Scopus database. Data including: manuscript title, authors, total citation count, level of evidence, journal, publication year, and country of publication was extracted from a final list of articles.
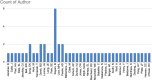
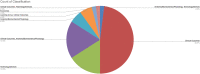
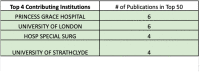
Results: The top 50 publications regarding robotic assisted arthroplasty were cited a total of 4530 times (including self-citations), with an average total of 91. The years with the most publications in the top 50 were: 2017, 2018, and 2019, producing 7, 6, and 5 papers, respectively. Only 4 papers in the top 50 were published prior to the year 2003. The most common level of evidence was level V, and the most common category was Clinical Outcomes (74%). The United States contributed half of the 50 articles, and Princess Grace Hospital and University of London were the most contributory institutions, each with 6 of the top 50 articles.
Conclusion: This analysis provides a comprehensive review of the most cited and influential papers in robotic-assisted arthroplasty. Understanding these trends in the literature will ultimately pave the way for physicians and researchers to continue to innovate and research in a targeted manner as they gain an understanding of what has been studied and what remains inadequately explored.
Level of evidence: 3.
Keywords: Arthroplasty; Bibliometric review; Robotic assisted arthroplasty; Robotic surgery.
© 2022 Professor P K Surendran Memorial Education Foundation. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Sloan M., Premkumar A., Sheth N.P. Projected volume of primary total joint arthroplasty in the U.S., 2014 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100(17):1455–1460. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee S., Cherian J.J., Elmallah R.K., Pierce T.P., Jauregui J.J., Mont M.A. Robot-assisted total hip arthroplasty. Expet Rev Med Dev. 2016;13(1):47–56. - PubMed
-
- Kayani B., Konan S., Tahmassebi J., Pietrzak J.R.T., Haddad F.S. Robotic-arm assisted total knee arthroplasty is associated with improved early functional recovery and reduced time to hospital discharge compared with conventional jig-based total knee arthroplasty: a prospective cohort study. Bone Joint Lett J. 2018;100-B(7):930–937. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials