Thirty years of research on physical activity, mental health, and wellbeing: A scientometric analysis of hotspots and trends
- PMID: 36016904
- PMCID: PMC9396383
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.943435
Thirty years of research on physical activity, mental health, and wellbeing: A scientometric analysis of hotspots and trends
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Thirty years of research on physical activity, mental health, and wellbeing: A scientometric analysis of hotspots and trends.Front Public Health. 2023 Mar 14;11:1178895. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1178895. eCollection 2023. Front Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36998283 Free PMC article.
Abstract
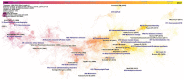
The sheer volume of research publications on physical activity, mental health, and wellbeing is overwhelming. The aim of this study was to perform a broad-ranging scientometric analysis to evaluate key themes and trends over the past decades, informing future lines of research. We searched the Web of Science Core Collection from inception until December 7, 2021, using the appropriate search terms such as "physical activity" or "mental health," with no limitation of language or time. Eligible studies were articles, reviews, editorial material, and proceeding papers. We retrieved 55,353 documents published between 1905 and 2021. The annual scientific production is exponential with a mean annual growth rate of 6.8% since 1989. The 1988-2021 co-cited reference network identified 50 distinct clusters that presented significant modularity and silhouette scores indicating highly credible clusters (Q = 0.848, S = 0.939). This network identified 6 major research trends on physical activity, namely cardiovascular diseases, somatic disorders, cognitive decline/dementia, mental illness, athletes' performance, related health issues, and eating disorders, and the COVID-19 pandemic. A focus on the latest research trends found that greenness/urbanicity (2014), concussion/chronic traumatic encephalopathy (2015), and COVID-19 (2019) were the most active clusters of research. The USA research network was the most central, and the Chinese research network, although important in size, was relatively isolated. Our results strengthen and expand the central role of physical activity in public health, calling for the systematic involvement of physical activity professionals as stakeholders in public health decision-making process.
Keywords: CiteSpace; evidence synthesis; mental illness; physical exercise; scientometrics.
Copyright © 2022 Sabe, Chen, Sentissi, Deenik, Vancampfort, Firth, Smith, Stubbs, Rosenbaum, Schuch and Solmi.
Conflict of interest statement
Author OS has received advisory board honoraria from Otsuka, Lilly, Lundbeck, Sandoz, and Janssen in an institutional account for research and teaching. Author JF has received consultancy fees from Parachute BH for a separate project. Author BS is on the Editorial Board of Ageing Research Reviews, Mental Health and Physical Activity, the Journal of Evidence Based Medicine and the Brazilian Journal of Psychiatry. Author BS has received honorarium from a co-edited a book on exercise and mental illness, advisory work from ASICS & ParachuteBH for unrelated work. Author MSo has received honoraria/has been a consultant for Angelini, Lundbeck and Otsuka. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

