Scutellarin Loaded on Ultradeformable Nanoliposome Scutellarin EDTMP (S-UNL-E) Promotes Osteogenesis in Osteoporotic Rats
- PMID: 36017130
- PMCID: PMC9398854
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1395299
Scutellarin Loaded on Ultradeformable Nanoliposome Scutellarin EDTMP (S-UNL-E) Promotes Osteogenesis in Osteoporotic Rats
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Scutellarin Loaded on Ultradeformable Nanoliposome Scutellarin EDTMP (S-UNL-E) Promotes Osteogenesis in Osteoporotic Rats.Stem Cells Int. 2023 Dec 20;2023:9851693. doi: 10.1155/2023/9851693. eCollection 2023. Stem Cells Int. 2023. PMID: 38152722 Free PMC article.
Abstract
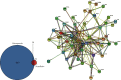
Scutellarin is known as a safe, effective, and low-cost traditional Chinese medicine and has a variety of biological activities. Studies reported that the scutellarin loaded on ultradeformable nanoliposome scutellarin EDTMP (S-UNL-E) could promote osteoblast differentiation and bone formation in vitro. However, its effect on promoting osteogenesis in vivo is still unclear. In this study, pharmacology network and transcriptome sequencing were used to screen the potential targets and pathways of scutellarin in treating osteoporosis. The female Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were operated on with bilateral oophorectomy and femoral defect to establish an osteoporosis model and then treated separately with bone dust, single scutellarin, 40 mg/kg ultradeformable nanoliposome scutellarin (S-UNL), and the optimal concentration of 40 mg/kg S-UNL-E for a total of 56 d to detect the parameters of trabecular bones. And qRT-PCR and western blot were performed to determine the expression of prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (PTGS2), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), transcription factor 4 (TCF4), and β-catenin. Results of microscopic computed tomography (Micro-CT) of trabecular bones showed that single scutellarin, S-UNL, and S-UNL-E all promoted the bone formation of osteoporotic rats, in which S-UNL-E manifested the most remarkable therapeutic effect. And it is found that 40 mg/kg of S-UNL-E increased the expression of PTGS2, ALP, TCF4, and β-catenin, which indicated that S-UNL-E stimulated the secretion of ALP in bone defect areas to promote bone healing, and increased PTGS2 expression thereby enhancing the transcription and translation of key gene β-catenin and TCF4 in the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway to treat osteoporotic rats.
Copyright © 2022 Minhua Teng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures



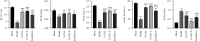

References
-
- Guo L., Guan Z., Huang Y., Wang Y., Shi J. The neurotoxicity of β-amyloid peptide toward rat brain is associated with enhanced oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis, all of which can be attenuated by scutellarin. Experimental and Toxicologic Pathology . 2013;65(5):579–584. doi: 10.1016/j.etp.2012.05.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Guo H., Hu L. M., Wang S. X., et al. Neuroprotective effects of scutellarin against hypoxic-ischemic-induced cerebral injury via augmentation of antioxidant defense capacity. The Chinese Journal of Physiology . 2011;54(6):399–405. - PubMed
-
- Zhu W., Liang G., Huang Z., Doty S. B., Boskey A. L. Conditional Inactivation of the CXCR4 receptor in osteoprecursors reduces postnatal bone formation due to impaired osteoblast development∗. The Journal of Biological Chemistry . 2011;286(30):26794–26805. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.250985. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

