Effects of Acupuncture Combined with Exercise on Expression of Immune Factors in Aging Rats and Its Significance in Antiaging Intervention
- PMID: 36017145
- PMCID: PMC9398838
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/6833196
Effects of Acupuncture Combined with Exercise on Expression of Immune Factors in Aging Rats and Its Significance in Antiaging Intervention
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Effects of Acupuncture Combined with Exercise on Expression of Immune Factors in Aging Rats and Its Significance in Antiaging Intervention.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Sep 27;2023:9827284. doi: 10.1155/2023/9827284. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 37811227 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: With the improvement of people's living standards, how to maintain health and delay aging to improve the quality of life and achieve longevity has become a hot topic of concern. objective. To investigate the effect of acupuncture combined with exercise on the expression of immune factors in aging rats and its significance in antiaging intervention.
Materials and methods: Forty-three SD rats included 12 rats in the control group, and the remaining rats were injected intraperitoneally with D-galactose 500 mg/kg to prepare a subacute aging rat model. The 24 rats that were successfully modeled were divided into acupuncture exercise groups and exercise groups according to the random number table method, with 12 rats in each group. After the modeling, the comparison group did not do any intervention, the exercise group was given aerobic exercise intervention, and the acupuncture exercise group was given acupuncture combined with exercise intervention. The effect of immune factor expression in rats was compared.
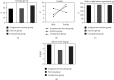
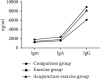
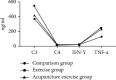
Results: The levels of IgM, IgA, and IgG in the acupuncture exercise group were significantly higher than those in the exercise group (P < 0.05). The IL-10 content in the acupuncture exercise group was significantly higher than that in the exercise group (P < 0.05) and was significantly reduced in the acupuncture exercise group compared with the comparison group (P < 0.05). The level of IL-6 in the acupuncture exercise group was significantly lower than that in the exercise group, and the level of IL-6 in the acupuncture exercise group was significantly increased compared with the comparison group (P < 0.05). The C3 and C4 levels in the acupuncture exercise group were significantly higher than those in the exercise group (P < 0.05). The levels of IFN-γ and TNP-α were significantly lower in the acupuncture exercise group than in the exercise group and significantly increased in the acupuncture exercise group compared with the comparison group (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Ling turtle eight method acupuncture combined with exercise promoted the development of immune organ spleen, enhances the body's immune function and complement system, inhibits the immune inflammatory response and regulates immune balance, reduces the inflammatory response caused by the aging of D-type galactose, and achieves the effect of delaying aging.
Copyright © 2022 Lulu Jiang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Effect of acupuncture of different acupoints on immune function in rats with exhausted swimming].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2011 Jun;36(3):181-6. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2011. PMID: 21793382 Chinese.
-
[Anti-inflammation mechanism of electro-scalp acupuncture in treatment of ischemic stroke based on IL-12 mediated JAK/STAT signaling pathway].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2022 Oct 12;42(10):1137-44. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20210821-0006. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2022. PMID: 37199205 Chinese.
-
[Rich selenium-Banqiao-Codonopsis Pilosula mixture enhances immune function of aging mice].Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015 Oct;31(10):1346-9. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015. PMID: 26429536 Chinese.
-
[Effect of Acupuncture Combined with Rehabilitation on Immune and Neural Functions in Elderly Patients with Stroke].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2018 Sep 25;43(9):567-72. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.170611. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2018. PMID: 30232865 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
[Acupuncture ameliorates neurological function by suppressing microglia polarization and inflammatory response after cerebral ischemia in rats].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022 Nov 25;47(11):941-48. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20210988. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022. PMID: 36453669 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Retracted: Effects of Acupuncture Combined with Exercise on Expression of Immune Factors in Aging Rats and Its Significance in Antiaging Intervention.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Sep 27;2023:9827284. doi: 10.1155/2023/9827284. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 37811227 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

