MiR-96-5p Facilitates Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Phenotypes by Inhibiting FHL1
- PMID: 36017148
- PMCID: PMC9398840
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/7891222
MiR-96-5p Facilitates Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Phenotypes by Inhibiting FHL1
Abstract
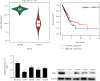
Objective: FHL1 is understood as a tumor repressor gene in various cancers and a possible target for cancer treatment. We investigated the influences of FHL1 on cell functions as well as its molecular mechanisms in lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) cells.
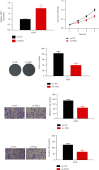
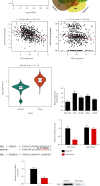
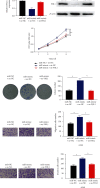
Methods: The miRNA-mRNA modulatory axis was predicted by bioinformatics. The expression levels of FHL1 mRNA and protein in LUAD cells were, respectively, analyzed by qRT-PCR and western blot. Dual luciferase analysis was introduced to verify the interaction between miR-96-5p and FHL1. CCK-8, cell colony formation, and Transwell assays were utilized to analyze proliferation, colony formation, migration, and invasion of A549 cells.
Results: Expression of FHL1 mRNA and protein in LUAD tissue and cells was downregulated, which was linked with poor prognoses of patients. In addition, FHL1 overexpression could hamper colony formation, proliferation, invasion, and migration of LUAD cells. In addition, dual-luciferase analysis verified miR-96-5p as an upstream regulator of FHL1. Overexpression of miR-96-5p suppressed FHL1 expression in LUAD cells and promoted proliferation, invasion, and migration of LUAD cells, while overexpression of FHL1 could simultaneously restore the above-mentioned promoting effect.
Conclusion: MiR-96-5p fostered cell malignant behaviors by targeting FHL1. This research uncovered the regulatory mechanism of FHL1 in LUAD and offered optional therapeutic targets for LUAD patients.
Copyright © 2022 Feng Zhou et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest in the article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of four and a half LIM domain protein 1 in tumors (Review).Oncol Lett. 2024 Oct 29;29(1):37. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14783. eCollection 2025 Jan. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39512507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-139-5p Inhibits Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion by Targeting MAD2L1.Comput Math Methods Med. 2020 Nov 4;2020:2953598. doi: 10.1155/2020/2953598. eCollection 2020. Comput Math Methods Med. 2020. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Sep 27;2023:9789647. doi: 10.1155/2023/9789647. PMID: 33204298 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
MiR-139-5p Targeting CCNB1 Modulates Proliferation, Migration, Invasion and Cell Cycle in Lung Adenocarcinoma.Mol Biotechnol. 2022 Aug;64(8):852-860. doi: 10.1007/s12033-022-00465-5. Epub 2022 Feb 18. Mol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35181869
-
miR-21-5p promotes lung adenocarcinoma cell proliferation, migration and invasion via targeting WWC2.Cancer Biomark. 2020;28(4):549-559. doi: 10.3233/CBM-201489. Cancer Biomark. 2020. PMID: 32623387
-
The role of FHL1 in tumors.Gene. 2024 Jun 15;911:148347. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2024.148347. Epub 2024 Mar 6. Gene. 2024. PMID: 38458365 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Role of four and a half LIM domain protein 1 in tumors (Review).Oncol Lett. 2024 Oct 29;29(1):37. doi: 10.3892/ol.2024.14783. eCollection 2025 Jan. Oncol Lett. 2024. PMID: 39512507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA‑mediated regulation in lung adenocarcinoma: Signaling pathways and potential therapeutic implications (Review).Oncol Rep. 2023 Dec;50(6):211. doi: 10.3892/or.2023.8648. Epub 2023 Oct 20. Oncol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37859595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A potential tumor marker: Chaperonin containing TCP‑1 controls the development of malignant tumors (Review).Int J Oncol. 2023 Sep;63(3):106. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2023.5554. Epub 2023 Aug 4. Int J Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37539774 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

